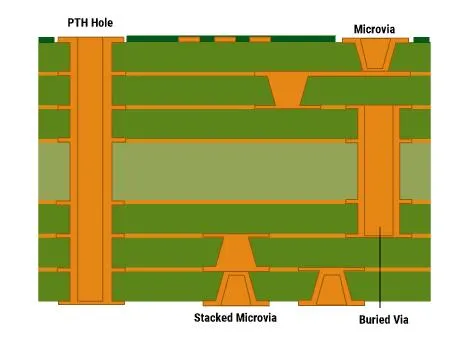
What is microvia?
Most PCBs are multilayer boards, and through holes are used to establish connections between each layer of the board. As the name suggests, microvia is the smallest through-hole with a size equal to or less than 150 microns drilled on PCB board by laser. In 2013, the IPC standard changed the definition of micro via to one with an aspect ratio of 1:1. The ratio of hole diameter to depth (not exceeding 0.25 mm). Previously, microvias were anything less than or equal to 0. 15 mm in diameter, so they usually span only a single layer.
Because the diameter is very small compared with the mechanical drilling through holes (PTH), we define them as microvias, which usually connect only one layer of the board to its adjacent layers.
These vias reduce the possibility of any type of manufacturing defect because they are laser drilled, thereby reducing the chance of any residue remaining after the process. Because of their small size and the ability to connect one layer to the next, they can make densely printed circuit boards that have more complex designs.
Microvia vs Via
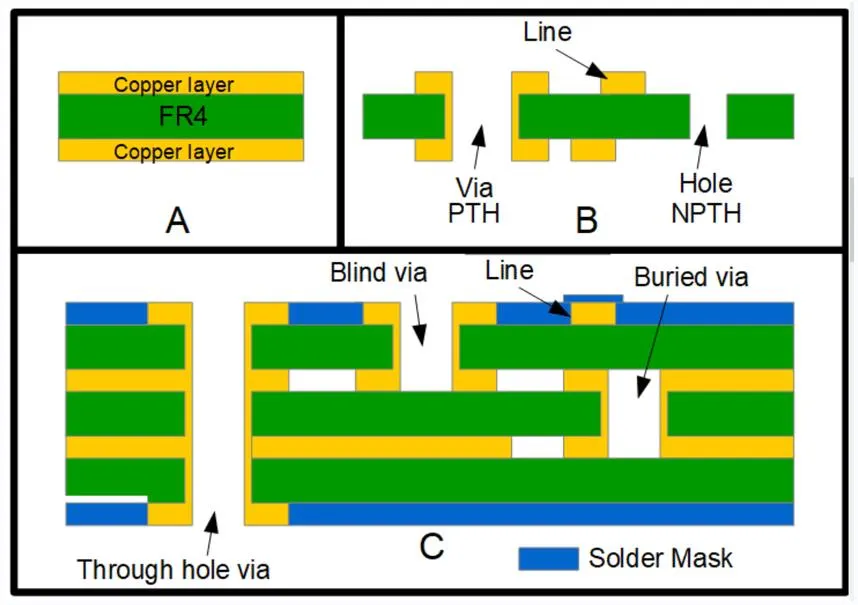
Generally, vias with a diameter of less than or equal to 6mils are called microvias, which need laser drilling equipment. The diameter of ordinary Via holes is generally 8-20 mils, and mechanical drilling is used.
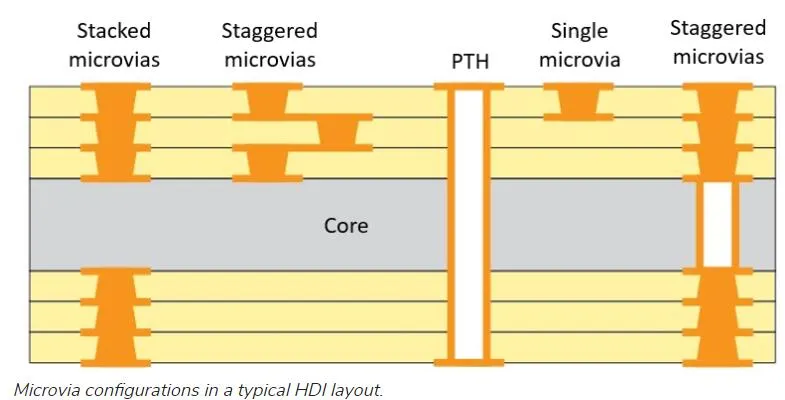
What are the types of microvias?
There are two types of microvias: stacked and staggered
These small structures enable the routing to reach the inner layer of PCB with higher interconnection density and a higher number of layers. These structures have existed for many years, but they are becoming more and more common in various systems where PCB needs to have multiple functions. If you have conducted a dimensional study and determined that about 6 million traces are required to install all components on a printed circuit board, it is inevitable that microvias will be used to route between the layers. This is how these structures are formed, and what you need to know about PCB microvias.
These holes are usually drilled by laser, and the process has been improved continuously. Due to their high output, they are the first choice in PCB manufacturing. The new development of laser drilling technology can reduce the number of micro holes to 15µm. The laser involved can only drill through one layer at a time. However, manufacturers use stacked microvias in multiple layers by drilling holes in individual layers and then stacking and compacting each layer.

In the PCB manufacturing process, compared with ordinary through holes, laser drilling micro through-holes have a lower possibility of manufacturing defects. This is because laser drilling does not leave any material in the hole. Mechanical drilling of micro through-holes may produce defects due to vibration caused by bit wear, while mechanical drilling of micro through-holes is only useful when the diameter is about 8 mils. In electroplating and reflow soldering, microvias do have the same risk as ordinary vias.
Therefore, it is very important to discuss the filling of tents or microvias with the manufacturer.
In addition to these qualities, the only differences between microvias are their typical diameter and their position on the circuit board. In this case, the distance between the balls is very small, and the dog bones will not be fanned out. The microvias on the surface layer can also be placed in the pad filled with conductive epoxy resin and plated with copper (called "VIPPO" or “POFV”). The advantage of the VIPPO copper structure is that the pad can be welded now, so it is an ideal choice for BGA with a spacing of about 4 mils.
Considering the distribution of microvia on the PCB, the following are different types of microvias.
Blind microvias
The blind microvias start from the surface layer and end in one or two layers below the surface. It is best to place only one blind pore covering only a single layer. If you need to span 2 layers, it is better to use stacked microvias because they will be more reliable and require fewer manufacturing steps.
Buried microvias
The buried microvias span between the two inner layers and do not reach any of the circuit board surfaces. Just like blind holes, it is better to use buried microvias to span single layers to ensure reliability and ease of manufacture.
Stacked microvias
Stacked microvias are just stacked buried vias or blind microvias stacked on top of buried microvias. This is the standard method to span multiple layers in HDI PCB. The internal buried pores in the stack need to be filled with conductive adhesive and plated to ensure firm contact when depositing and plating the next via in the stack.
These types of micro vias have some special advantages in saving space and EMI.
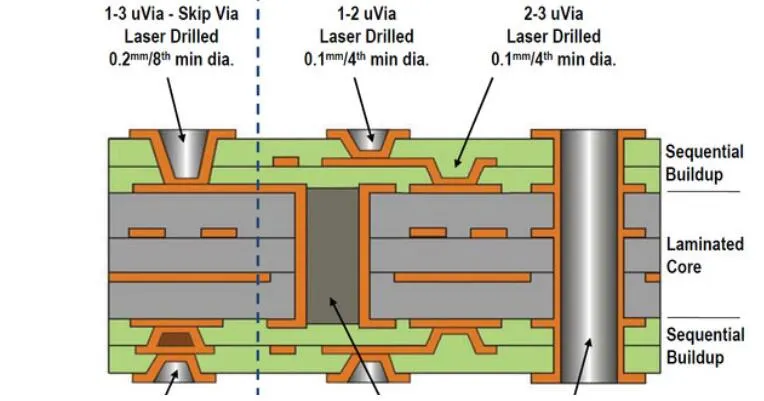
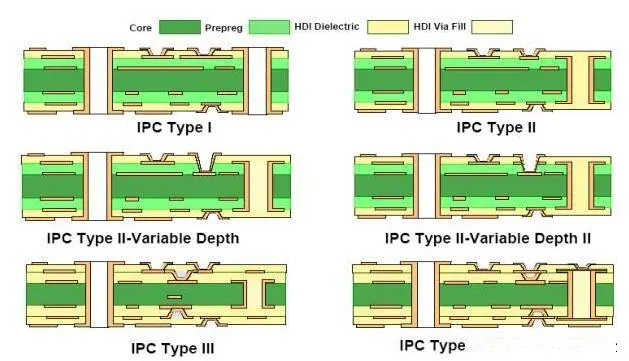
In IPC-2226, high-density interconnects are classified into six design types. They are grouped by stack characteristics in the following categories: type I, type II, type III, type IV, type V, and type VII
Type I, 1 [C] 0 or 1 [C] 1 with through holes from surface to surface.
Type II, 1 [C] 0 or 1 [C] 1, with via embedded in the core and possibly via connecting the outer layer from the outer surface to another surface.
Type III, 2 [C] 0, two or more HDI layers are added to the through-holes of the core or from one surface to another.
Type IV, 1 [P] 0, where p is a passive substrate without electrical connection.
V-type coreless construction using layer pairs.
Type VI uses layer pairs as an alternative to coreless construction.
What exactly are blind and buried vias?
A blind Vias connects the outer layer to one or more inner layers, but doesn’t go through your whole PCB.
A buried vias connects two or more inner layers, but won’t go through to the outer layer. It is buried within the circuit and completely internal. So it is totally not visible to the naked eyes.
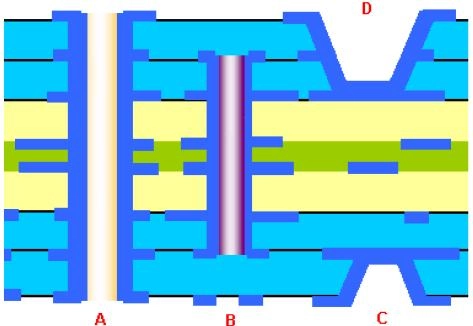
A: Through hole via B: Buried via C and D: Blind Via
What are blind and buried vias advantages?
Blind and buried vias can help you to meet the high density constraints of lines and pads on a typical design without increasing the overall layer count or your board size
The vias also help you manage the printed circuit board aspect ratio and limit the change of break out
What are blind and buried vias Disadvantages?
Cost is still the main issue with boards using blind and buried vias, compared to the boards using standard through hole vias. The high cost is due to the increasing complexity of the board and more steps in the manufacturing process. At the same time, testing and precision checks are made more frequently.
Venture engineers can look at your engineering requirements, space needs and the functionality of your PCB to help you reduce costs with buried and/or blind vias.
What are blind and buried vias applications?
In most cases, blind and buried vias are designed in high-density circuit boards (HDI-PCB). HDI PCB (High-density interconnect printed circuit board) is a fast growing part of the PCB industry. It has a higher circuitry density per unit than traditional PCBs. In the past, computers used to fill up an entire room, but now, with HDI technology, you can find HDI boards in laptops, cellphones and watches, as well as other portable consumer electronics such as digital cameras and GPS devices. HDI PCBs play an important role in providing us with a more efficient life.
HDI PCB use a combination of blind and buried vias, as well as micro vias , with our state –of- the-art laser drilling machine (Mitsubishi), laser direct imaging (LDI), we are able to provide you fast delivery services for HDI PCB prototypes. Please check below for our HDI PCB manufacturing capabilities.
| HDI PCB Feature | technical specification |
| layers counts | 4 – 30 layers |
| HDI builds | 1+N+1, 2+N+2, 3+N+3,4+N+4, any layer in R&D |
| Materials | FR4, Halogen free FR4, Rogers |
| Copper weights (finished) | 18μm – 70μm |
| Minimum track and gap | 0.075mm / 0.075mm |
| PCB thickness | 0.40mm – 3.20mm |
| Maxmimum dimensions | 610mm x 450mm |
| Surface finishes available | OSP, Immersion Gold(ENIG), Immersion tin, Immersion silver, Electrolytic gold, Gold fingers |
| Minimum mechanical drill | 0.15mm |
| Minimum laser drill | 0.1mm advanced |




