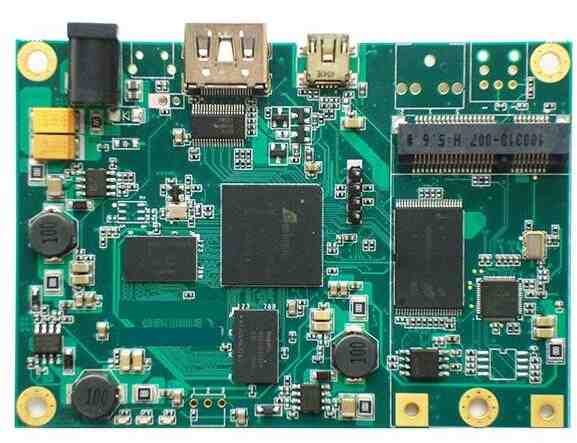
PCB board copying, that is, on the premise that there are physical electronic products and circuit boards, reverse analysis of circuit boards is carried out by using reverse R&D technology, and PCB files, bill of materials (BOM) files, schematic files and other technical documents of original products as well as PCB silkscreen production documents are carried out. 1: 1, and then use these technical documents and production documents for PCB board making, component welding, fly needle testing, circuit board debugging, and complete the complete copy of the original circuit board template. This paper introduces the PCB board copying industry will be involved in the future technology Wi-Fi 6 RF technology.
1. Introduction to key Technologies of 802.11ax
802.11ax (also known as Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5 refers to 802.11ac) is proposed to meet the user speed and experience requirements in high-density scenarios. Similar to the application scenario of eMBB in 3GPP 5G NR, its purpose is to improve the user rate in high-intensive scenarios, so as to obtain better user peak data experience. In March 2013, TG (Task Group) working group was established. In 2014, it began to study the 802.11ax standard. In 2016, the initial draft of 802.11ax was proposed, and the standard was officially released in 2019.
Table 1. Main differences between physical layer parameters of 802.11ax and the previous two generations of technology
Compared with previous generations of technology, 802.11ax has the following new features:
(1) Expanded the coverage of the signal. Since the per symbol duration of 802.11ax is increased from 3.2us to 12.8us, the longer transmission time can reduce the terminal packet loss rate and resist multipath fading. In addition, 802.11ax can at least use 2MHz bandwidth for narrowband transmission, effectively reduce the frequency band noise interference, improve the terminal acceptance sensitivity, and increase the coverage distance.
(2) The modulation mode is increased by 1024QAM, and the combination of MCS10 and MCS11 is proposed to improve the single-stream air port throughput. 802.11ac uses 256QAM and transmits 8 bits of data per symbol (28=256). 802.11ax uses 1024QAM and transmits 10bit of data per symbol bit (210=1024). The increase from 8 to 10 is 25%, which means that 802.11ax has a 25% increase in single-space stream data throughput over 802.11ac. Empty port throughput =1/(symbol + protection) time × coding efficiency × modulation order × number of effective subcarriers =1/(12.8us+0.8us)×5/6×10×980≈600Mbit/s
(3) The maximum number of space streams is 8, and uplink MU-MIMO is introduced. Compared with 802.11ac, upstream data does not need to be transmitted independently on a single node. MU-MIMO can be used for both upstream and downstream.
(4) Following the example of 3GPP LTE, 11ax introduces OFDMA multiple access technology and calls the smallest sub-channel "Resource Unit (RU)". Different users use different RU for data communication. From the perspective of total time-frequency resources, multiple users send data at the same time on each time slice, which improves the utilization rate of the channel.
(5). 802.11 adopts Carrier sense collision detection (CSMA/CA) as the MAC layer protocol, which means that only one radio device can transmit on the network at the same time. If an 802.11 terminal detects a transmission signal (the Header in the PHY layer) from another 802.11 terminal, it will delay the transmission.
Similar to the scrambling code used to distinguish base stations in WCDMA, 802.11ax introduces a new same-frequency transmission recognition mechanism called BSS Coloring mechanism. Add BSS color field to PHY packet header to "color" the data from different BSS, and assign a color to each channel. The color indicates a group of basic service sets (BSS) that do not interfere with each other. The receiving end can recognize the interference signal of the same frequency transmission as early as possible and stop receiving, so as to avoid wasting the time of the transceiver. If the color is the same, it is considered to be the interference signal in the same BSS, and the transmission will be delayed. If the colors are different, there is no interference between the two devices, and the two Wi-Fi6 devices can transmit in parallel on the same channel and frequency. In a network designed this way, channels of the same color are so far apart from each other that they are less likely to interfere with each other.
(6) Protocol compatibility: 802.11ax requires compatibility with previous 802.11a/b/h/n/ac. The 802.11ax protocol is forward compatible with 802.11n and 802.11a, so its frame format, in addition to data leads, includes the regular lead compatible with 802.11n and the efficient lead compatible with 11ax. Regular leads include L-STF (short training field), L-LTF (long training field), and L-sig words:
1) L-STF is mainly used for data synchronization;
2) L-LTF is mainly used for rough frequency offset estimation;
3) L-sig contains some user and frame data. An important function of L-sig is to distinguish between regular frames and 802.11ax frames. L-sig is repeated for 802.11ax frames and vice versa for regular frames. It also has an important function to tell the encoding mode and frame length of the base station transmitter.









