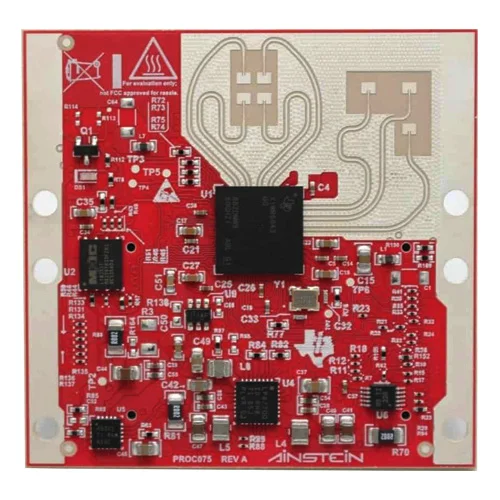
XWR6843 mmWave sensing device PCB Assembly
Name: FR4-based PCB substrate Assembly
Wide field of view antenna: Azimuth FOV 120°, Elevation FOV 80°
Discrete DCDC power management solution
Relaxed PCB rules: Lower manufacturing cost
– No micro vias, only through via
– No vias on the BGA pads
Serial port for onboard QSPI flash programming
60-pin, high-density (HD) connectors for raw analog-to-digital converter (ADC) data over LVDS:Onboard CAN-FD transceiver;USB powered standalone mode of operation
Millimeter wave: Electromagnetic waves with a wavelength of 1 to 10 millimeters are called millimeter waves. They are located in the wavelength range where microwaves and far-infrared waves overlap, so they have the characteristics of both spectra. The theory and technology of millimeter wave are the extension of microwave to high frequency and the development of light wave to low frequency.
On June 15, 2020, Liu Yunjie, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, said that Nanjing Network Communication and Security Purple Mountain Laboratory has developed a CMOS millimeter wave fully integrated 4-channel phased array chip.
Introduction to mmWave
There is no precise definition of the millimeter wave frequency band. Usually, the electromagnetic wave in the frequency domain of 30~300GHz (wavelength 1~10mm) is called millimeter wave. It is located in the wavelength range where microwave and far infrared wave overlap, so there are two kinds of characteristics of the spectrum. The theory and technology of millimeter wave are the extension of microwave to high frequency and the development of light wave to low frequency.
Millimeter wave characteristics
Compared with light waves, millimeter waves have less attenuation when propagating through the atmospheric window (when millimeter waves and submillimeter waves propagate in the atmosphere, some attenuation due to resonance absorption of gas molecules is minimal), and are affected by natural light and The influence of heat radiation source is small.
Advantage:
Extremely wide bandwidth. It is generally believed that the millimeter wave frequency range is 26.5-300GHz, and the bandwidth is as high as 273.5GHz. More than 10 times the full bandwidth from DC to microwave. Even considering atmospheric absorption, only four main windows can be used when propagating in the atmosphere, but the total bandwidth of these four windows can reach 135GHz, which is 5 times the sum of the bandwidths of the microwave bands below. This is undoubtedly very attractive in today's tight frequency resources.
The beam is narrow. The millimeter wave beam is much narrower than the microwave beam under the same antenna size. For example, a 12cm antenna has a beam width of 18 degrees at 9.4 GHz, but only 1.8 degrees at 94 GHz. Therefore, it is possible to distinguish small objects that are closer together or to observe the details of objects more clearly.
Compared with lasers, the propagation of millimeter waves is much less affected by climate, and can be considered to have all-weather characteristics.
Compared with microwaves, millimeter wave components are much smaller in size. So mmWave systems are easier to miniaturize.
Shortcoming:
①The propagation attenuation is serious in the atmosphere.
②The processing precision of the device is high.
Millimeter wave propagation characteristics
Millimeter waves have a large number of applications in the fields of communication, radar, remote sensing and astronomy. In order to successfully design and develop a millimeter-wave system with excellent performance, it is necessary to understand the atmospheric propagation characteristics of millimeter-wave under different meteorological conditions. Factors affecting the propagation characteristics of millimeter waves mainly include: molecular absorption (oxygen, water vapor, etc.) , and the environment (including vegetation, ground, obstacles, etc.), the combined effect of these factors will cause the millimeter wave signal to be attenuated, scattered, change the polarization and propagation path, and then introduce new noise in the millimeter wave system. Factors will greatly affect the operation of mmWave systems, so we must study the propagation characteristics of mmWave in detail.
Millimeter wave radar
In recent years, with the increasing demand for millimeter-wave systems, millimeter-wave technology has made major breakthroughs in the development of transmitters, receivers, antennas, and millimeter-wave devices, and millimeter-wave radar has entered a new stage of various applications.
Since the 1980s, due to the increasing demand for millimeter-wave radars, there has been an upsurge in the development of millimeter-wave radars, which depends on the following characteristics of millimeter-wave radars:
①Extremely wide frequency band, suitable for various broadband signal processing;
②A narrow beam can be obtained under a small antenna aperture, with good directivity, extremely high spatial resolution, and high tracking accuracy;
③Wide Doppler bandwidth, obvious Doppler effect, good Doppler resolution, high speed measurement accuracy;
④The impact of ground clutter and multipath effects is small, and the low-altitude tracking performance is good;
⑤The millimeter-wave scattering characteristics are sensitive to the details of the target shape, so it can improve the ability and imaging quality of multi-target discrimination and target recognition;
⑥Since the millimeter-wave radar emits with a narrow beam, it is difficult for the enemy to intercept in electronic countermeasures;
⑦At present, the stealth frequency range of stealth aircraft and other target designs is limited to 1~20GHz, and because the uneven parts such as the body are more obvious than millimeter waves, these unevenness will cause angular reflection, thereby increasing the effective reflection area, so millimeter wave Radar has a certain anti-stealth function;
⑧Compared with laser and infrared, millimeter wave does not have the high resolution of the latter, but it has the ability to penetrate smoke, dust and fog, and can work around the clock.
The disadvantage of millimeter-wave radar is mainly affected by atmospheric attenuation and absorption, and the current operating range is mostly limited to within 10 kilometers. In addition, compared with microwave radar, the components and parts of millimeter wave radar are currently mass-produced with low yield. In addition, many devices need to be coated with gold or silver in the millimeter wave frequency band, so the cost of the device is relatively high.
Millimeter wave antenna
①Horn Antenna
The general opening waveguide of the pyramidal horn can radiate electromagnetic waves, but due to the small aperture, the radiation efficiency and gain are low. If the opening of the metal waveguide is gradually enlarged and extended, a horn antenna is formed. Horn antennas are widely used in microwave and millimeter wave bands because of their simple structure, wide frequency band, easy manufacture and convenient adjustment. It is also widely used in millimeter wave therapeutic equipment.
②Microstrip antenna
Microstrip antennas or printed antennas were first widely used in the centimeter wave band, and then extended to the millimeter wave band. This kind of expansion is not scaled down proportional to the wavelength, not a complete imitation, but a new concept and new development.
However, millimeter-wave microstrip antennas have two key problems. One is that the loss of the transmission line becomes larger, and the other is that the dimensional tolerance becomes very strict.
③Leaky wave antenna
This type of antenna radiates energy due to some discontinuous structures when the electromagnetic wave is transmitted along the open structure, so it is called a leaky wave antenna.
Kingford provides XWR6843 mmWave sensing device PCB Assembly services. This is a PCBA one-stop assembly factory with senior industry experience. Welcome to inquiry.
Name: FR4-based PCB substrate Assembly
Wide field of view antenna: Azimuth FOV 120°, Elevation FOV 80°
Discrete DCDC power management solution
Relaxed PCB rules: Lower manufacturing cost
– No micro vias, only through via
– No vias on the BGA pads
Serial port for onboard QSPI flash programming
60-pin, high-density (HD) connectors for raw analog-to-digital converter (ADC) data over LVDS:Onboard CAN-FD transceiver;USB powered standalone mode of operation