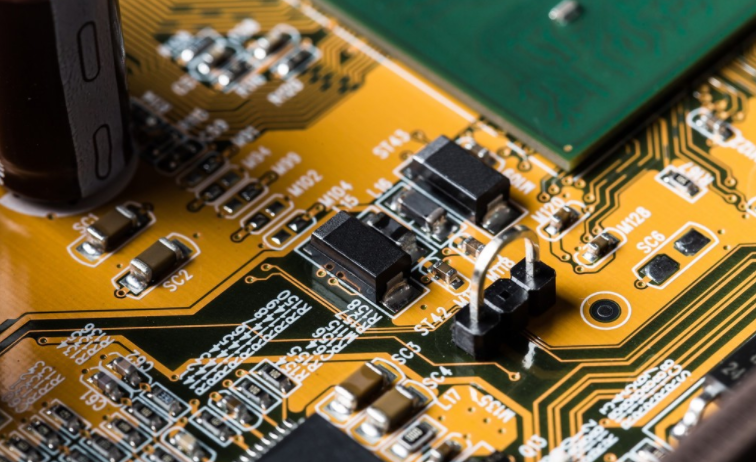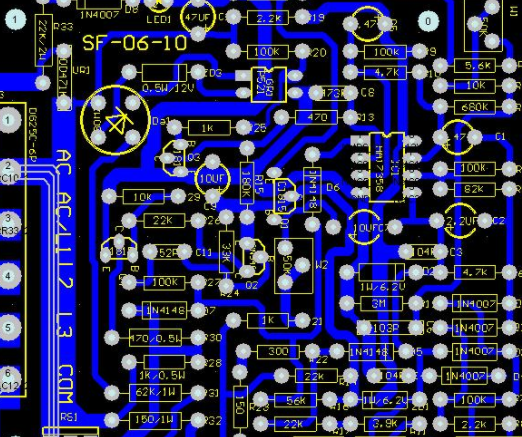
Layout and wiring principle of RF PCB
In general, layout and wiring rules PCB board must be understood by everyone However, do you all know the design rules of RF boards PCB boards? Today, let's talk about the layout and wiring principle of RF board PCB board
RF board PCB board layout principle
1) Layout determination: Before layout, you should have a detailed understanding of the function, working frequency band, current and voltage of the circuit board, main RF equipment types, EMC and related RF quota, and define the stack structure, impedance control, external structure size, mask cavity and cover. The size and location of the equipment, and the handling instructions for special equipment (such as the size and location of the equipment that needs to be hollowed out and directly cooled by the mainframe shell). In addition, the number of power, heat dissipation, gain, isolation, sensitivity, etc. of main RF equipment, as well as the connection of filtering, bias and matching circuits should also be specified. For power amplifier circuits, impedance matching circuit guidelines are obtained for matching wiring requirements recommended in the device manual or RF field analysis software simulation.
2) Physical partition: The key is to arrange the main components according to the flow direction of the main signal of the board. First, fix the component on the RF path according to the location of the RF port, and adjust its direction to reduce the length of the RF path to. In addition to the general layout rules, it is also necessary to consider how to reduce mutual interference and anti-interference capability of each component to ensure full isolation of multiple circuits. For circuit modules with insufficient isolation or sensitive and strong radiation sources, consider using metal masks to mask the RF energy in the RF area.
3) Power partition: The layout is generally divided into three parts: power supply, digital and analog, which must be separated in space. The layout and wiring cannot cross regions. The strong and weak current signals shall be separated as far as possible, and the digital and analog signals shall be separated. The circuits that complete the same functions shall be arranged within a certain range as far as possible, so as to reduce the signal loop area.
PCB board
Wiring principle of RF board PCB board
1) Keep the digital circuit away from the analog circuit as much as possible, ensure that the RF track points to the large area grounding plane, and run the RF track on the surface as much as possible.
2) Digital and analog signal lines are not routed across areas. If the RF wiring must pass through the signal wire, it is better to connect the grounding to the main grounding along the RF wiring between them; The second option is to ensure that the RF wiring is connected to the main ground. Pass through the signal line to reduce capacitive coupling, while placing as much ground as possible around each RF track and connecting to the main ground. Generally, RF printing lines should not be in parallel or too long. If parallel connection is indeed required, an earth wire should be added between the two conductors (the earth wire should be drilled to ensure good grounding). RF differential line, parallel line, and two parallel lines plus grounding wire (the grounding wire is drilled to ensure good grounding). The characteristic impedance of the printed line is designed according to the equipment requirements.
3) The basic sequence of RF PCB wiring is: RF line – baseband RF interface line (IQ line) – clock line – power supply part – digital baseband part – grounding.
4) Considering the influence of green oil on the efficiency and signal of the microstrip line, it is recommended that the high frequency microstrip line should not be coated with green oil, and the medium and low frequency single board microstrip line should be coated with green oil.
5) RF traces are usually not perforated. If the RF path must be changed, the size of the through-hole should be reduced to, which not only reduces the path inductance, but also reduces the possibility of RF energy leakage to other areas in the laminate.
6) Duplexer, IF amplifier and mixer always have multiple mutually interfering RF/IF signals. RF and IF traces should be crossed as far as possible, and a ground should be separated between them.
7) Except for special purposes, it is prohibited to protrude too many wire ends on the RF signal track.
8) The wiring of baseband RF interface line (IQ line) should be wider, greater than 10mil. In order to avoid phase error, the line length should be as equal as possible and the spacing should be as same as possible.
9) The RF control line shall be wired as short as possible, and the wiring length shall be adjusted according to the input and output impedance of the transmission control signal equipment to reduce the introduction of noise. Keep traces away from RF signals, nonmetallic vias and "grounded" edges. Do not drill ground vias around the trace to prevent signals from coupling to the RF ground through the vias.
10) Keep digital wiring and power wiring away from RF circuit as far as possible; Clock circuit and high-frequency circuit are the main sources of interference and radiation, which must be arranged separately from sensitive circuits.
11) The main clock wiring is required to be as short as possible. It is recommended that the line width is greater than 10mil, and both sides of the line are grounded to prevent interference from other signal lines. Ribbon routing is recommended.
12) The control line of the voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) must be kept away from the RF signal