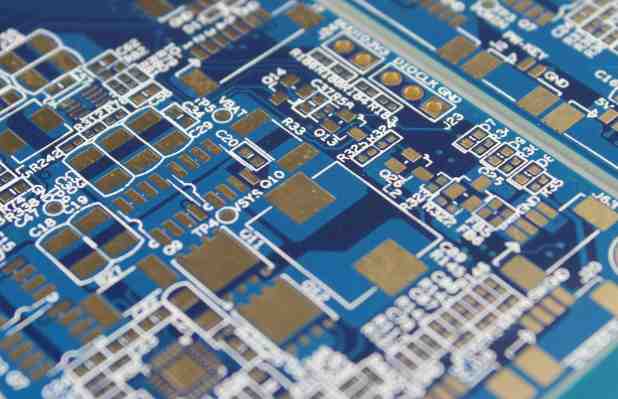
First, SMT assembly requirements for surface coating
1. Comply with laws and regulations (ROHS China ROHS).
2. Weldability: heat resistance, welding temperature, wetting, shelf life.
3. Protection: anti-oxidation ability.
4. Reliability: internal stress, defects, life of solder joints.
5. Cost: materials, equipment, manpower, wastewater treatment, yield.
6. Scope of application: compatible with solder resistance, suitable for PCB circuit board varieties (such as rigid torsion board), no Pb.
7. Environmental protection: easy to handle, no smoke, pollution.
Second, each surface treatment introduction
1. Lead-free spray tin
Process: Micro-etching - water washing - high temperature flux coating - tin spray - water washing. (Some circuit board manufacturers preheat the board before micro-etching)
Process: When the PCB board is sprayed with tin, it is immersed in molten lead-free solder (about 270 ° C), quickly lift the PCB board, and the hot air knife (temperature 265-270 ° C) blows the liquid solder from the front and back of the board, so that the crescent-shaped solder on the copper surface is flattened, and the solder is prevented from bridging.
Equipment: horizontal, vertical lead-free hot levelling machine. (Horizontal type obtained more uniform coating, automatic production).
Materials: Lead-free solder such as SnCuNi, SnCuCo, SnCuGe or 305 solder. High temperature resistant flux.
Requirements: The surface of the pad 2-5 microns, the hole should be less than 25 microns (also relaxed to 38 microns).
Features: The coating layer is not flat enough, mainly suitable for wide lines, large welding plate, HDI board is usually not used. High requirements on heat resistance of copper-clad plate. The tin-spraying process is dirty, smelly, and dangerous when operated at high temperature. Its use is subject to certain restrictions.
2.OSP (organic solderable protectant)
Also known as preflux (heat-resistant preflux), it is the continuation and development of the early rose-scented flux.
Process: oil removal - micro-etching - pickling - pure water washing -OSP- cleaning - blow drying.
Principle: A layer of organic film is formed on the surface of copper, which firmly protects the surface of fresh copper and can prevent oxidation and pollution at high temperatures. OSP thickness 0.1-0.2 microns, or 0.2-0.5 microns.
Features: simple process, low cost, can be used in low-technology PCB circuit boards, but also can be used in high-density chip packaging substrate. It is the most promising surface coating process. (Controversial points: unclear color during assembly, OSP is similar to copper color, scratches the board, affects welding, OSP storage period of about 6 months)
At present, OSP can withstand thermal stress (288℃, 10s) three times, without oxidation, without discoloration.
3. Chemical tin
Process: oil removal - micro-etching - pickling - pure water washing - tin sinking - cleaning.
Features: Since all solder is currently based on tin, the tin layer can be compatible with any kind of solder. From this point of view, sunken tin has good development prospects in the comparison of several varieties of PCB surface coating.
Thickness: 1.0±0.2 micron.
Cons:
Can not withstand multiple welding, the interface compound formed after a welding will become a non-weldable surface.
It will produce tin whiskers, which will affect reliability.
The solder solution is easy to attack the solder resistance film, making the film dissolve and change color, resulting in reverse corrosion of the copper layer.
High settling temperature, ≥60℃, 1 micron tin layer needs to settle for 10 minutes.
Use: Some customers specify, with a settled tin coating, than the lead-free spray tin layer flat. Communication motherboard applicable. The tin plate should be stored in a good room and used during the storage period.
4. Chemical silver
Process: oil removal (degreasing) - micro-etching - pickling - pure water washing - silver sinking - cleaning.
Features:
The process is simple, fast and the cost is not high.
Ag solution contains some organic matter, anti-silver layer discoloration, silver migration.
Coating thickness 0.1-0.5 micron (usually 0.1-0.2 micron) excellent welding performance.
The silver layer has good inspectability (silvery white) when assembled.
Cons:
The water used in the whole Ag production line is pure water. The anti-silver layer turns yellow and black. (There are chloride ions in tap water, Ag+Cl AgCl, resulting in white precipitation)
Silver combines easily with sulfur in the air to form silver sulfide, yellow or black. All operation, storage, packaging, need to wear sulfur free gloves, sulfur free paper packaging, storage environment requirements are high. It is not allowed to use ordinary paper to separate the boards, and it is not allowed to use rubber bands to wrap the boards.
Anti-silver ion migration, has sunk silver plate shall not be stored in a humid environment, during the storage period to use.
Application: Customer specified. In high frequency signal, the electric performance of the submerged Ag plate is good. Many users in Europe and the United States require sinking Ag board.
5. Electroplating nickel gold
Process: oil removal - micro-etching - pickling - pure water washing - nickel plating - pure water washing - gold plating - gold recovery - water washing.
Coating type:
① Hard gold plating
Use: PCB plug, button on.
Features:
Wear-resistant, good contact, hardness (120-190㎏ / ㎜2)
Nickel base, Ni layer thickness 3-5 microns; Gold thickness: 0.1,0.25,0.5,0.8,1.0... One micrometer.
Gold plating contains metals such as cobalt (Co, 0.5%), or Ni antimony.
② Plated soft gold, pure gold, 24K gold
Application: Welding.
Features:
Nickel base, ≥2.5 microns, prevent the diffusion of gold layer to copper layer, nickel layer firmly combined with the solder during welding.
Au plating layer is very thin, 0.05-0.1 micron.
Cons:
The line has to be plated with gold, the cost is high, and it is rarely used at present.
Solder resistance printed on the gold surface is easy to fall off.
The gold layer becomes brittle when welded. (Gold content in solder ≥ 3%)
6. Chemical Nickel Gold (ENIG)
Process: oil removal (degreasing) - micro-corrosion - activation - chemical nickel - chemical gold - cleaning.
Features:
Electroless Ni/Au coating has uniform thickness, good coplanarity, good weldability, excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance. Widely used in flashlight, computer and other fields.
The thickness of the nickel layer is 3-5 microns, the purpose is to prevent the mutual diffusion between the copper-gold interface and ensure the reliable welding of the solder joint.
Chemical Ni/Au has rapidly replaced electroplating Ni/Au.
Chemical nickel is the key to the process, but also the biggest difficulty.
The gold layer is usually 0.05-0.15 micron.
Reaction mechanism:
Nickel ① ide
The copper surface is catalyzed by palladium, and nickel plating reaction begins by reducing agent and nickel ion in solution. Nickel itself is the catalyst for further electroless nickel plating, and under the action of sodium hypophosphate, a reducing agent in the solution, the chemical nickel deposition process will continue until the product is removed from the tank.
In the deposition process, phosphorus is co-deposited with nickel into the coating, and the chemical precipitation of nickel is actually a chemical precipitation of nickel-phosphorus alloy.
demi-gold
REDOX reaction. Gold is deposited on the surface of nickel by Ni-au replacement reaction.