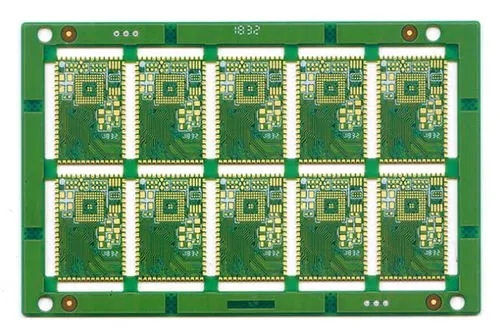
What is the controlled impedance of a circuit board?
When you use complex circuit boards, you need to ensure that your circuit boards provide the high performance you need. An important factor to consider is the impedance of the circuit board. The impedance of control circuit boards can improve their functions.
What is the controlled impedance?
Controlled impedance is a method of determining the resistance of a circuit to alternating current in advance. The resistance is a function of the resistance and reactance in the circuit. Impedance is critical to the operation of a circuit because it affects the schedule for the circuit to complete its functions. It affects the timing and integrity of basic processes. Controlling the impedance by changing the physical structure of the circuit board components to give a specific value of impedance helps the circuit board operate in the way it is designed. Controlled impedance is usually a PCB design consideration for high-frequency analog circuits or high-speed digital circuits.
Impedance (usually in ohms) is a circuit characteristic that must be noted during PCB design. The resistance and reactance of the circuit have a significant impact on the function, because some processes must be completed first to ensure normal operation. When these operations are not performed as planned, the command chain will destroy the system and cause complete failure. Printed circuit boards with impedance requirements will counteract the voltage changes that occur and cause the equipment or small tools to operate as expected.
The use of differential impedance PCB components provides the control required for a range of products. We can recommend software programs for detecting resistance and reactance current to provide you with the required specifications. MCL will use this data to create a custom PCB. The resulting circuits are cost-effective and provide higher reliability.
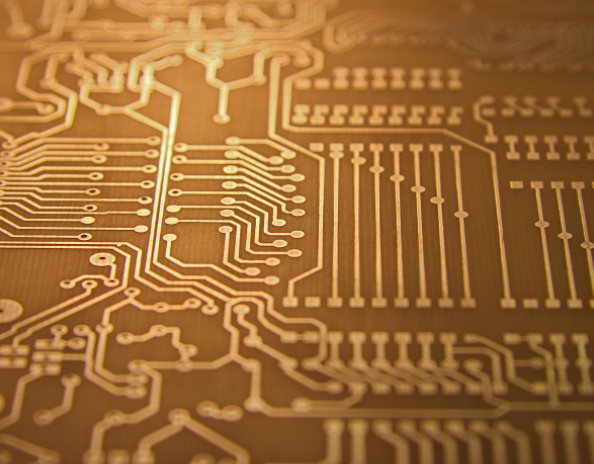
How does PCB impedance control work?
Before deciding which impedance control service is required for a printed circuit board, you need to know the basics of impedance control. What exactly is impedance control and how does it work? PCB impedance control is divided into three basic service levels:
Impedance free control: In this case, you do not need any additional design elements to ensure the correct impedance, because your impedance tolerance is very loose. Naturally, this will lead to faster completion and cheaper circuit boards, as manufacturers do not have to include any special measures.
Impedance observation: What is impedance observation? In this case, the designer will outline the impedance control wiring, and the PCB supplier will adjust the wiring width and dielectric height accordingly. Once the manufacturer has approved these specifications, they can begin to manufacture the circuit board. You can apply for a time domain reflectometer (TDR) test to confirm the impedance for a fee.
Impedance control: Actual impedance control is usually required only when your design has strict impedance tolerance, which may be difficult to achieve when it first appears. When the manufacturer's capacity constraints approach the dimensional requirements, it is difficult to ensure the target impedance at the initial attempt.
Impedance control in pcb manufacturing process
In the case of impedance control, the manufacturer makes the circuit board do its best to achieve the target impedance. They then run a TDR test to see if it was successful. If not, they will adjust accordingly and retry until the required impedance is reached.