About OSP film thickness control and PCB storage
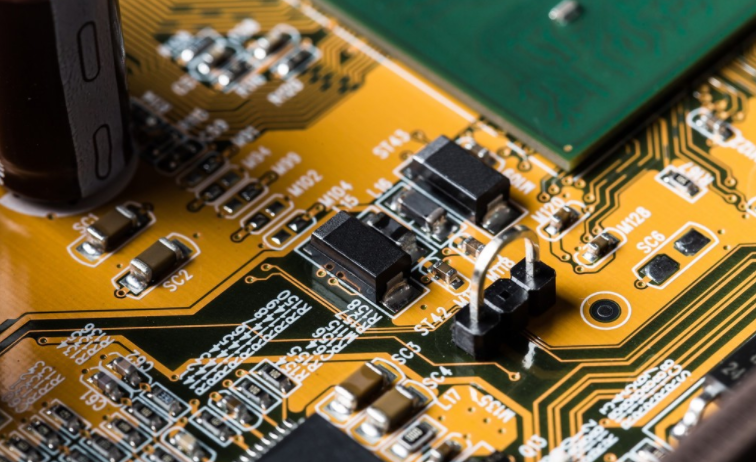
OSP is the abbreviation of (Organic Solderability Preservatives), which is translated into Chinese as organic solderability preservatives, also known as copper protectors, or English notice Its function is to lock moisture, prevent liner oxidation, and maintain good solderability on the copper surface Because OSP has good surface flatness, high reliability of solder joints, relatively simple PCB manufacturing process and low cost, it has obvious advantages over other surface treated PCBs, and is becoming more and more popular in the industry Under normal conditions, OSP surface treated PCB has good tin efficiency. For example, improper use of PCB production process control or SMT control will lead to poor soldering According to the characteristics of OSP surface treated PCB and the analysis of bad welding cases, this paper focuses on the analysis of the factors affecting PCB solderability, PCB storage and SMT use from the perspective of OSP film thickness control, and puts forward corresponding improvement measures
Circuit board
Printed circuit board is an indispensable material for modern electronic products With the rapid development of surface mount technology (SMT) and integrated circuit (IC) technology, PCB needs to meet the requirements of high density, high flatness, high reliability, small aperture, smaller requirements for PAD development, and higher requirements for PCB surface treatment and manufacturing environment OSP surface treatment is now a common PCB surface treatment technology It is a chemical method to grow a 5 um organic film on 0.2~0. clean bare copper surface This film resists oxidation at room temperature Thermal shock resistance and moisture resistance can protect copper surface from oxidation or vulcanization In the subsequent high-temperature welding, this protective film must be easily removed by the flux, exposed to the clean copper surface in a short time, and combined with the molten solder to form a solid solder joint Compared with other surface treatments, OSP surface treatment has the following advantages and disadvantages:
a. The OSP surface is flat and even, with a film thickness of 0.2~0.5um, which is suitable for SMT closely spaced component PCB;
b. OSP film has good thermal shock resistance, which is suitable for lead-free technology and single board and double board processing, and is compatible with any solder;
c. Water soluble operation, temperature can be controlled below 80 ℃, which will not cause bending deformation of the substrate;
D. Good operation environment, less pollution and easy automation of production line;
e. The process is relatively simple, with high yield and low cost;
f. The disadvantage is that the protective film formed is very thin, and the OSP film is easy to scratch (or scratch);
G. After PCB has been welded at high temperature for many times, the OSP film (referring to the OSP film on the solderless pad) will change color, crack, thin and oxidize, affecting the solderability and reliability;
h. Syrup formulations are diverse, with varying efficacy and quality.
2. Problem description
In the actual production process, OSP boards are prone to surface discoloration, uneven film thickness (too thick or too thin); In the later stages of PCB production, if the PCB is stored and used improperly, the formed PCB is prone to welding problems such as solder pad oxidation. The tin on the mat is too poor to form a solid solder joint, and the solder is insufficient; SMT production of double-sided plates and welding of the second side of the tin furnace are easy to lead to poor reflow welding, solder joint leakage, appearance not meeting the IPC 3 standard, and high solder furnace welding failure rate