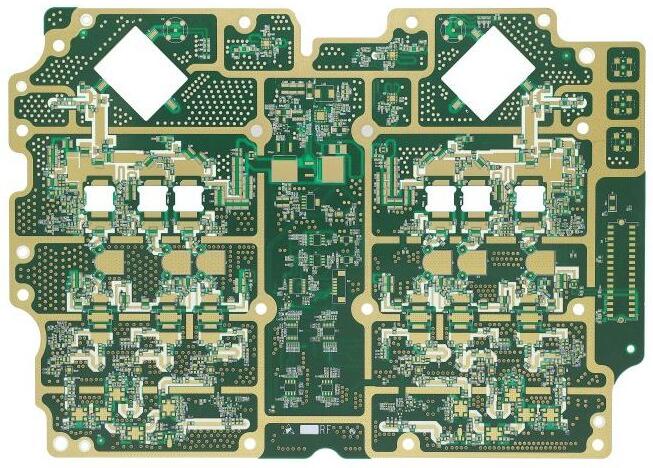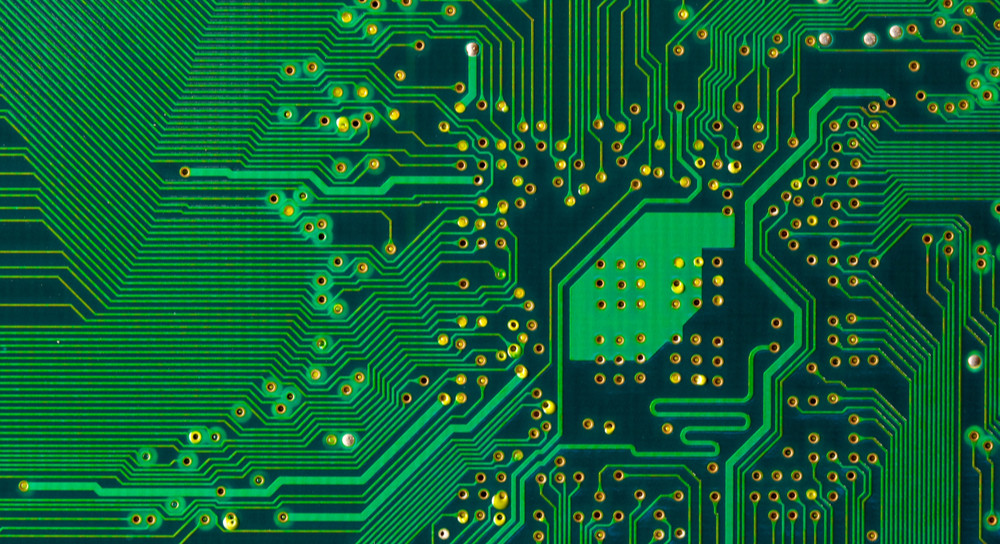
Methods and Technologies for Controlling PCB Etching Process
Process printed circuit board (PCB) is a relatively complex physical and chemical reaction process from light-emitting plate to circuit graphics This paper will analyze the last step of etching
At present, the typical processing technology of printed circuit board (PCB) is "pattern electroplating". That is to say, a layer of lead tin anti-corrosive coating is pre coated on the copper foil part (i.e. the pattern part of the circuit) that needs to be reserved on the outer layer of the circuit board, and then the remaining copper foil is chemically etched, which is called etching.
Etch Type
It should be noted that there are two layers of copper on the circuit board during the etching process. In the outer layer etching process, only one layer of copper must be completely etched, and the rest will form the final required circuit. The characteristic of this pattern electroplating is that the copper plating layer only exists below the lead tin resistance layer.
Another process is to plate copper on the whole circuit board, while the part outside the photosensitive film is only tin or lead tin resist. This process is called "full plate copper plating process". Compared with pattern electroplating, the biggest disadvantage of copper plating on the entire circuit board is that all parts of the circuit board must be copper plated twice, and all parts must be corroded during the etching process. In this case, when the wire width is very thin, a series of problems will occur. At the same time, the side corrosion will seriously affect the uniformity of the line.
PCB assembly
In the processing technology of external circuits, there is another method for printed circuit boards, that is, to use a photosensitive film instead of a metal coating as an resist layer This method is very similar to the inner layer etching process. You can refer to the etching in the inner layer manufacturing process
At present, tin or lead tin is the most commonly used anti-corrosion coating for the etching process of amino etchant. Amino etchant is a common chemical liquid, which has no chemical reaction with tin or lead tin. Ammonia etchant mainly refers to ammonia/ammonium chloride etching solution.
In addition, ammonia/ammonium sulfate etching chemicals are also available on the market. After using sulfate based etching solution, the copper can be separated by electrolysis, which can be reused. Due to its low corrosion rate, it is rarely seen in actual production, but it is expected to be used for chlorine free etching.
Someone tried to use hydrogen sulfate as an etchant to etch the outer pattern. Due to many reasons such as economy and waste liquid treatment, this process has not been widely used in commercial sense. In addition, sulfuric acid hydrogen peroxide cannot be used for the etching of lead tin resist, and this process is not the main method of PCB external production. In fact, most people rarely care about it.
Etching quality and previous problems
The basic requirement for etching quality is to completely remove all copper layers except the one under the resist layer, which is called it. Strictly speaking, if accurate definition is required, the etching quality must include consistency of line width and undercut degree. Due to the inherent characteristics of the current etching solution, the etching effect is produced not only in the downward direction, but also in the left and right directions. This side etching is almost inevitable.
Undercut is one of the etching parameters often discussed. It is defined as the ratio of undercut width to etching depth, which is called etching factor. In the printed circuit industry, it has a wide range of changes, from 1:1 to 1:5. Obviously, smaller undercut or lower etching factor is the most satisfactory.
The structure of the etching equipment and the different components of the etching solution will affect the etching factor or the degree of side etching, or can be controlled from an optimistic point of view. The use of certain additives can reduce the degree of side erosion. The chemical composition of these additives is usually a trade secret, and developers will not disclose it to the outside world.
In many ways, etching quality exists long before the printed board enters the etching machine. Since various processes or printed circuit processing processes have very close internal relations, there is no process that is not affected by other processes and does not affect other processes. Many problems identified as etching quality actually exist in the process of removing the film, even before.
In addition, in many cases, due to the formation and dissolution of the reaction, in the printed circuit industry, the residual film and copper may also form and accumulate in the corrosive liquid, and plug in the nozzle of the corrosion machine and the acid resistant pump, which must be closed for processing and cleaning., This will affect work efficiency.
Equipment adjustment and interaction with corrosion solution
In the processing of printed circuits, ammonia etching is a relatively fine and complex chemical reaction process. On the other hand, this is an easy job. Once the process is upgraded, production can continue. The key is to keep the continuous working state after startup. Drying and stopping are not recommended. The etching process depends to a large extent on the good working conditions of the equipment. At present, no matter what etching solution is used, high-pressure spraying must be used. In order to obtain a cleaner line side and high-quality etching effect, nozzle structure and spraying method must be strictly selected.
In order to obtain good side effects, many different theories have emerged, forming different design methods and equipment structures. These theories are often very different. However, all etching theories recognize the most basic principle, even if the metal surface contacts with fresh etching solution as soon as possible. The chemical mechanism analysis of the etching process also confirmed the above viewpoint. In ammonia etching, assuming that all other parameters remain unchanged, the etching rate is mainly determined by ammonia (NH3) in the etching solution. In this case, there are two main purposes for etching the surface with fresh solution: one is to wash the newly generated copper ions; The other is to continuously provide ammonia (NH3) required for the reaction.
In the traditional knowledge of the printed circuit industry, especially the suppliers of printed circuit raw materials, people realize that the lower the content of monovalent copper ions in ammonia etching solution, the faster the reaction speed. This has been proved by experience. In fact, many ammonia based etching solution products contain special ligands (some complex solvents) of monovalent copper ions, which are used to reduce the monovalent copper ions (these are the technical secrets of their products with high reactivity). It can be seen that the influence of monovalent copper ions is not small. Reducing the unit price of copper from 5000 ppm to 50 ppm will more than double the etching rate.
Since a large number of monovalent copper ions are generated during the etching reaction, and since the monovalent copper ions are always closely bound with the complexing group of ammonia, it is difficult to keep their content close to zero. The univalent copper can be removed by converting the univalent copper into bivalent copper through the action of oxygen in the atmosphere. This can be achieved by spraying.
This is the functional reason for allowing air to enter the etch box. However, if the air is too much, it will accelerate the loss of ammonia in the solution, reduce the pH value, and lead to a decrease in the etching rate. Ammonia in the solution is also a change that needs to be controlled. Some users adopt the method of passing pure ammonia into the etching tank. Therefore, a set of PH meter control system must be added. When the PH value measured automatically is lower than the given value, the solution will be added automatically.
In the related field of chemical etching (also known as photochemical etching or PCH), the research work has begun and has reached the stage of etching machine structure design In this method, the solution used is bivalent copper, non ammonia copper etching It can be used in the printed circuit industry In PCH industry, the typical thickness of etched copper foil is 5 to 10 mils, and in some cases, the thickness is quite large Its requirements for etching parameters are generally higher than those of PCB industry