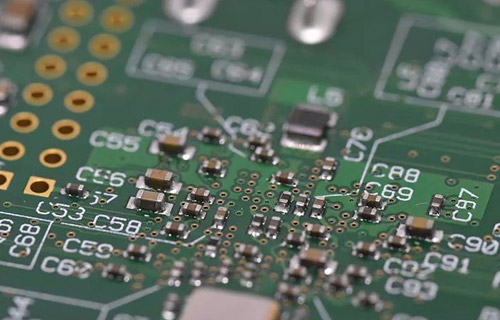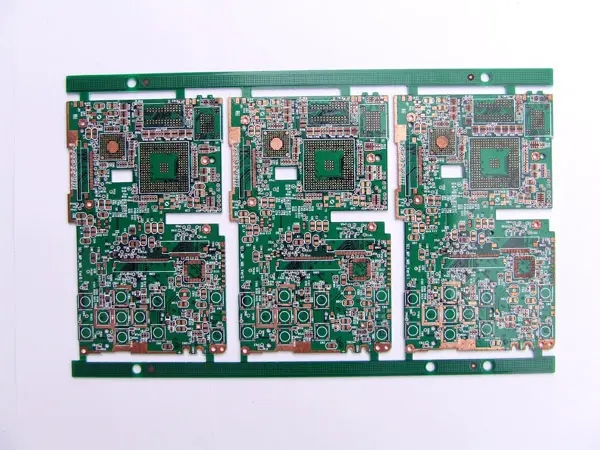
FPC Technology and Data Development and Technology Trend
Basic structure of FPC
The basic structure of a single side FPC In the case of traditional FPC, the copper foil conductor is fixed on the base film (such as polyimide), an adhesive (such as epoxy resin) is inserted on the base film, and then the etched circuit is covered with a protective film The structure uses adhesives such as epoxy resin Because of its high mechanical reliability, this floor is still one of the commonly used standard structures even now However, the heat resistance of adhesives such as epoxy resin or acrylic resin is lower than that of polyimide resin matrix film, so it becomes a bottomleneck that determines the upper limit of the use temperature of the entire FPC (Bottom Neck)
In this case, it is necessary to exclude the flexible circuit board structure of adhesives with low heat resistance. This configuration not only minimizes the thickness of the entire FPC, greatly improves the mechanical efficiency, such as bending resistance, but also helps to form fine circuits or multilayer circuits. The data of cohesionless copper clad laminate consisting only of polyimide layer and conductor layer have been put into practical use, which expands the selection range of data applicable to various purposes.
There is also a flexible circuit board with a double-sided through hole structure or a multi-layer structure in the flexible circuit board. The basic structure of the dual sided circuit of the flexible circuit board is roughly the same as that of the rigid circuit board. Adhesive is used for bonding between layers. However, the latest high-performance FPCs do not include adhesives, and only use polyimide resin to form copper clad laminate. There are many examples. The layer composition of flexible circuit board multilayer circuit is much more complex than that of printed circuit board. They are referred to as multilayer rigid or multilayer flexure. Adding layers will reduce flexibility, and reducing the number of layers used for bending or eliminating adhesion between layers can increase the freedom of mechanical movement. In order to manufacture multilayer rigid flexible plates, many heating processes are required, and the materials used must have high heat resistance. The use of non adhesive copper clad laminate is being increased.
Circuit board
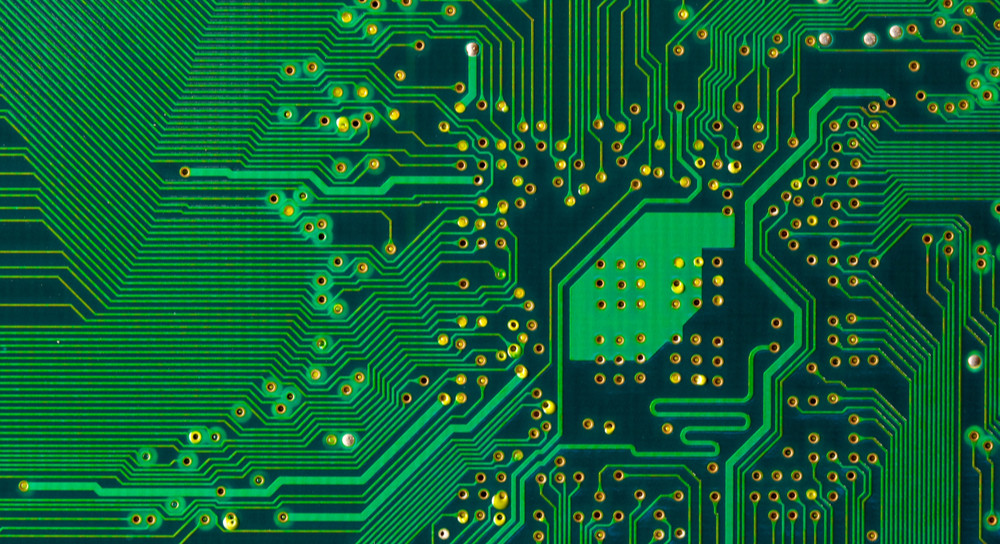
FPC Technology Trends
With the diversification and compactness of applications, FPCs used in electronic equipment need high-density circuits and high performance. Recent changes in FPc circuit density. Subtraction (etching) can be used to form single-sided circuits with conductor spacing of 30um or less, and double-sided circuits with conductor spacing of 50um or less have also been put into practical use. The diameter of through-hole between conductor layers connecting double-sided circuits or multilayer circuits is becoming smaller and smaller. At present, the through-hole diameter below 100um has reached the scale of mass production.
Based on the viewpoint of manufacturing technology, the possible manufacturing range of high-density circuits is analyzed. According to the circuit spacing and through hole diameter, high-density circuits can be roughly divided into three types: (1) traditional FPC; (2) High density FPC; (3) Ultra high density FPC.
In the traditional subtraction, FPC with spacing of 150um and through-hole diameter of 15um has been produced in batches. Due to the improvement of data or processing equipment, 30um circuit spacing can be processed even in subtraction. In addition, due to the introduction of CO2 laser or chemical etching and other processes, the mass production and processing of through-hole with a diameter of 50um can be realized. Most high-density FPCs produced in mass at present are processed through these technologies.
However, if the screw pitch is less than 25um and the through-hole diameter is less than 50um, it is difficult to improve the yield even if the traditional process is improved, and new processes or materials must be introduced. There are many processing methods for this process, but the semi additive method using electroforming (sputtering) technology is the most appropriate method. Not only are the basic processes different, but also the data and auxiliary materials used are different.
On the other hand, the progress of FPC connection technology requires FPC to have higher reliability and efficiency. With the increase of circuit density, the performance of FPC is required to be diversified and high performance. These performance requirements largely depend on circuit processing technology or the data used.
Basic composition information of FPC
The basic composition information of FPC is the base film or heat-resistant resin constituting the base film, followed by the copper clad plate and protective layer constituting the conductor.
Copper clad plate
Many FPC manufacturers usually purchase in the form of CCL, and then use CCL as the starting material to process them into flexible PCB products. FPC copper clad laminate or protective film (coating film) using the first generation polyimide film is made of an adhesive, such as epoxy or acrylic resin. The heat resistance of the adhesive used here is lower than that of the polyimide, and the heat resistance or other physical properties of the FPC are limited.
In order to avoid the disadvantages of traditional adhesive based CCL, high-performance FPCs including high-density circuits use adhesive free CCL. So far, there are many manufacturing methods, but the following three methods can be used in practice:
1) Casting process
The casting process starts with copper foil. The liquid polyimide resin is directly coated on the surface active copper foil and heat treated to form a film. The polyimide resin used here must have good adhesion to copper foil and good dimensional stability, but no polyimide resin can meet these two requirements. First, a thin layer of polyimide resin (adhesive layer) with good adhesion is coated on the surface of active copper foil, and then a certain thickness of polyimide resin with good dimensional stability is coated on the adhesive layer (core layer). Due to the different thermophysical properties of these polyimide resins, if the copper foil is etched, large pits will appear in the base film. In order to prevent this phenomenon, an adhesive layer is coated on the core layer to obtain good symmetry of the base layer.
In order to manufacture double-sided copper clad laminate, the adhesive layer uses thermoplastic (hot melt) polyimide resin, and then the copper foil is laminated on the adhesive layer by hot pressing.
2) Sputtering/electroplating process
The starting material of sputtering/electroplating process is a heat-resistant film with good dimensional stability. The first step is to use the sputtering process to form a seed layer on the surface of the activated polyimide film. The seed layer can ensure the bonding strength with the conductor base layer, and at the same time, it plays the role of electroplating the conductor layer. Nickel or nickel alloys are usually used. To ensure conductivity, a thin layer of copper is sputtered on a nickel or nickel alloy layer, and then copper is plated to the specified thickness.
3) Hot pressing method
The hot pressing method is to coat thermoplastic resin (thermoplastic adhesive resin) on the surface of heat-resistant polyimide film with good dimensional stability, and then laminate the copper foil on the hot melt resin at high temperature. Composite polyimide film is used here.
This composite polyimide film can be purchased from professional manufacturers, and the manufacturing process is relatively simple. When manufacturing copper clad laminate, the composite film and copper foil are laminated together and hot pressed at high temperature. The equipment investment is relatively small, suitable for small batch and multi variety production. The double-sided copper clad laminate is also easier to manufacture.
Other important material element constructing the FPC is the protective layer (Cover Layer). Now, various protection materials have been put forward The first practical protective layer is to apply the same heat-resistant film as the substrate and use the same adhesive as the CCL This structure is characterized by good symmetry, and it still occupies the main part of the market, commonly known as "film coating" However, it is difficult to automate the processing of this film protective layer, which increases the overall manufacturing cost. Because it is difficult to perform fine window processing, it cannot meet the requirements of high-density patches, which has become the mainstream in recent years