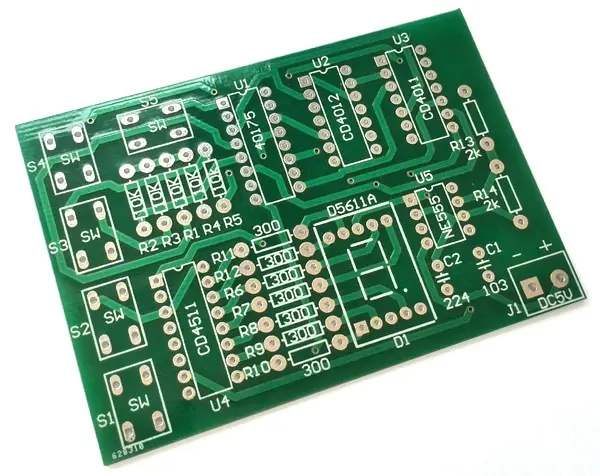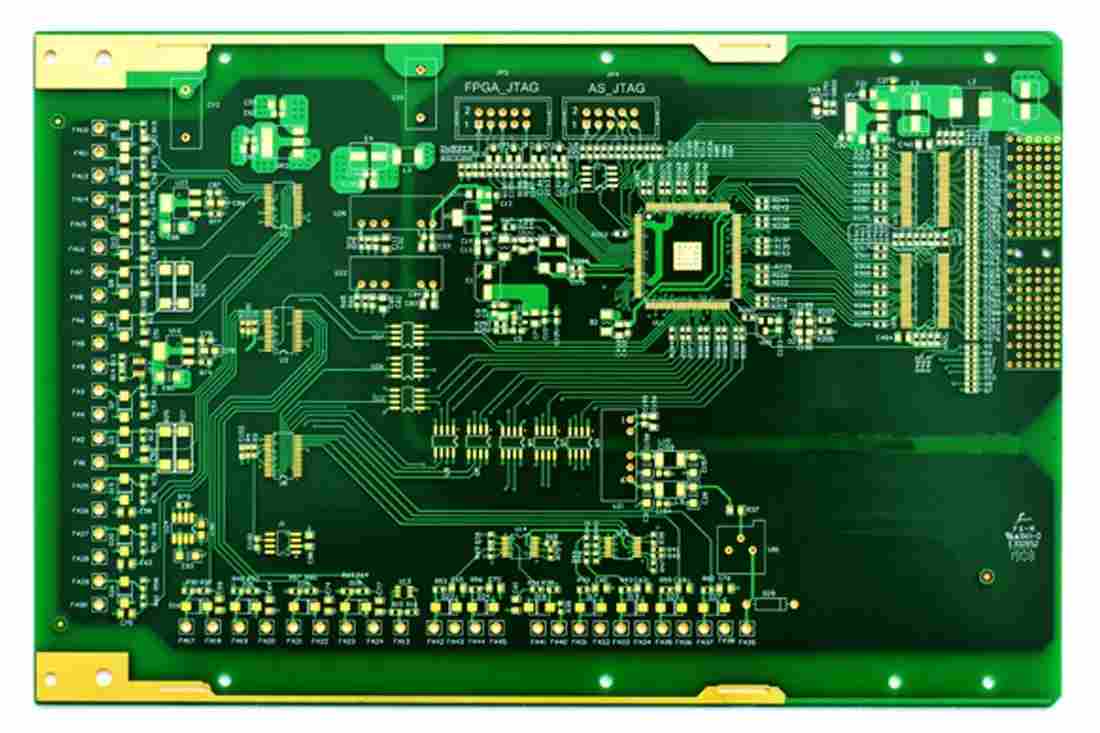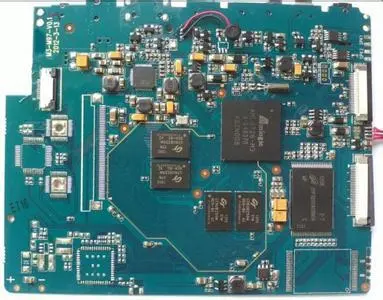
PCB design according to PCB pad requirements is to achieve the minimum diameter, which is at least 0.5mm larger than the maximum diameter of the keyhole flange at the welding terminal Test pads must be provided for all nodes according to ANSI/IPC 2221. Nodes refer to the electrical connection between two or more components
The design according to PCB pad requirements is to achieve the minimum diameter, which is at least 0.5mm larger than the maximum diameter of the keyhole flange of the welding terminal Test pads must be provided for all nodes according to ANSI/IPC 2221. Nodes refer to electrical connection points between two or more components A test pad requires a signal name (node signal name), x-y coordinate axis related to the reference point of the printed circuit board, and the coordinate position of the test pad (indicating which side of the printed circuit board the test pad is located on) It is necessary to provide SMT with the data of fixed devices, and also need the temperature closing technology of PCB assembly layout to promote the testability in the circuit with the help of the "fixed device for circuit test" or commonly referred to as the "nail bed fixed device". To achieve this goal, it is necessary to:
1) The diameter of the test pad specially used for detection shall not be less than 0.9mm.
2) The space around the test pad shall be greater than 0.6mm but less than 5mm. If the height of the component is greater than 6.7 mm, the test pad shall be placed 5 mm away from the PCB component.
3) Do not place any components or test pads within 3mm from the edge of the printed circuit board.
4) The test PCB pad shall be placed in the center of a 2.5mm hole in a grid. Where possible, standard probes and a more reliable fixture are permitted.

5) Do not rely on the edge of the connector pointer for pad testing. The test probe can easily damage the gold plated pointer.
6) Avoid plated through holes - probe both sides of the printed circuit board. Put the test tip through the hole on the non PCB components/welding surface of the PCB.