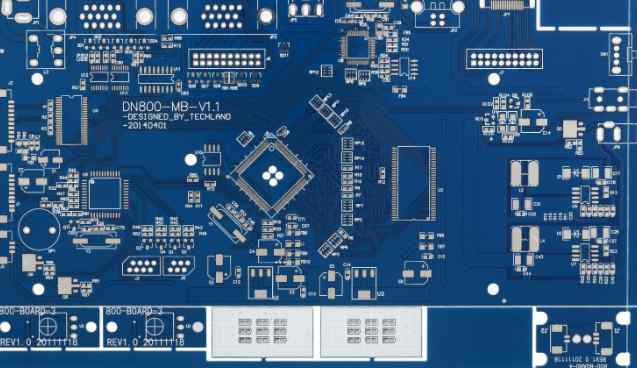
PCB inspection standards mainly include the following aspects:
a. Standards set by each country;
b. Military standards for each country;
c. Industry standard such as SJ/T10309;
d. PCB inspection operation instructions formulated by equipment supplier;
e. Technical requirements marked on PCB design drawings.
For PCBS that have been identified as keyboards in the device, these key characteristic parameters and indicators must be centralised and checked from the head in addition to regular inspection. To the toes.
Inspection item
Regardless of the type of PCB, they must go through similar quality inspection methods and items. According to the inspection method, the quality inspection items usually include visual inspection, general electrical performance inspection, general technical performance inspection and metallization inspection.
• Visual inspection
Visual inspection is simple with the help of a ruler, vernier caliper or magnifying glass. The inspection contents include:
a. Plate thickness, surface roughness and warping.
b. Appearance and assembly dimensions, especially those compatible with electrical connectors and rails.
c. The integrity and clarity of conductive patterns and the presence of bridging short circuits, open circuits, burrs or voids.
d. The quality of the surface, presence of pits, scratches or pinholes in the printed line or pad. Position of pad through holes and other through holes. The holes should be checked for missed or incorrect punching, whether the through-hole diameter meets the design requirements, and whether there are nodules and voids.
f. Pad quality and firmness, roughness, brightness and voids of raised defects.
g. Coating quality. Whether the coating flux is uniform and firm, whether the position is correct, whether the flux is uniform, and whether the color meets the requirements.
h. Quality of character, such as whether they are firm, clean and clean, no scratches, penetration or disconnection.
• General electrical performance check
There are two types of tests under this type of inspection:
a. Connection performance test. In this test, multimeters are commonly used to check the connectivity of conductive patterns, through the focused metallization through holes of double-sided PCBS and the connection performance of multilayer PCBS. For this test, PCBCart provides a general check before each manufactured PCB leaves its warehouse to ensure the implementation of its basic functionality.
B.I nsulatingperformancetest. This test is designed to check the insulation resistance of the same plane or between different planes to ensure the insulation performance of the PCB.
• General technical inspection
General technical checks include solderability and plating adhesion checks. For the former, check the wettability of the solder to the conductive pattern. The latter can be checked by qualified tips that are first glued to the plating surface to be checked and then quickly pulled out after even pressing. Next, the plating surface should be observed to ensure that no shedding occurs. In addition, some checks can be selected according to the actual situation, such as copper foil anti-fall strength and metallized anti-tensile strength.
• Metallization by inspection
The quality of metallized holes plays an important role in double-sided PCB and multilayer PCB. A large number of failures of electrical modules and even the whole equipment are due to the quality of metallized holes. Therefore, it is very necessary to pay more attention to the inspection of metallized holes. Metallization inspection includes the following aspects:
a. The metal plane of the through-hole wall should be complete and smooth, with no voids or nodules.
b. The electrical performance shall be checked according to the short and open circuit of the pad and the resistance between the metallization, through-hole and lead through the plating surface. After the environmental test, the resistance change rate of the hole should not exceed 5% to 10%. Mechanical strength refers to the bonding strength between the metallized through hole and the pad. The metallographic analysis test checks the quality of the plating surface, the thickness and uniformity of the plating surface, and the bonding strength between the plating surface and the copper foil.
Metallization is usually a combination of visual and mechanical inspection. The visual inspection is to observe that the PCB is placed in the light and the complete smooth through-hole wall is able to reflect the light evenly. However, passing through the wall containing the nodules or voids is not as bright. For mass production, inspection should be carried out by online testing equipment such as flying needle tester.
Due to the complex structure of multi-layer PCB, once a problem occurs, it is difficult to quickly locate the fault in the subsequent unit module assembly test process. Therefore, the inspection of its quality and reliability must be very strict. In addition to the above conventional inspection items, other inspection items include the following parameters: conductor resistance, metallized through hole resistance, inner short circuit and open circuit, insulation resistance between wires, bonding strength of electroplating surface, adhesion, thermal shock resistance, impact resistance, mechanical impact, current strength, etc. Each indicator must be obtained through the application of specialized equipment and methods.