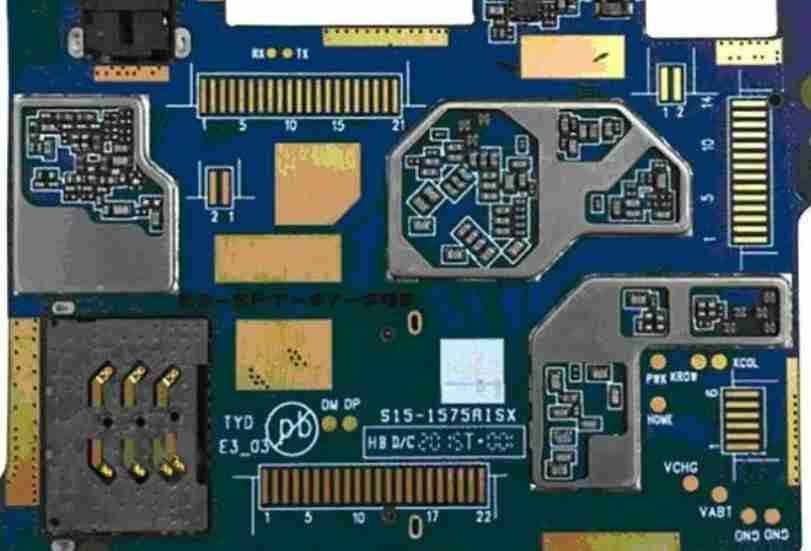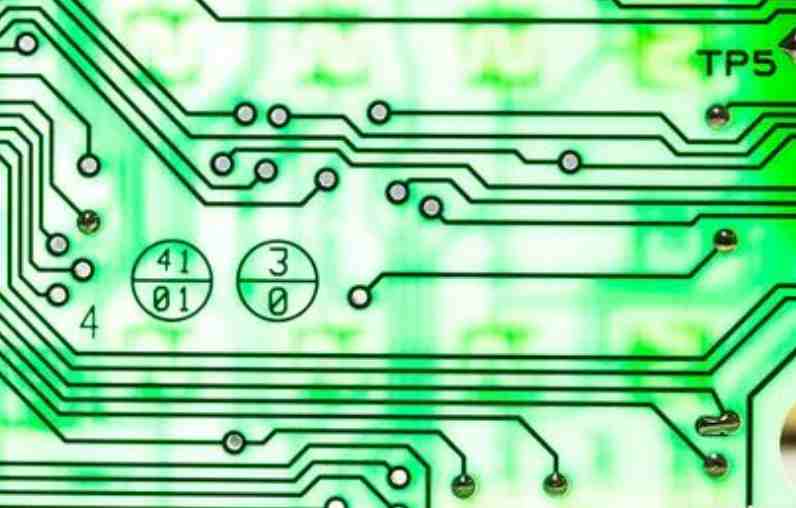
Electronic products are supported by rigid printed circuit boards (PCBS), which are used to provide a mechanical substrate for different electronic components of a particular product. Rigid PCBS utilize connection paths or wiring etched onto a laminated substrate (non-conductive). The etching of the channels is done using copper plates.
How to Design Rigid Printed Circuit Boards:
To design a high performance rigid printed circuit board, you will need to perform the following steps:
Design of rigid circuit boards using inkjet or laser printers.
Always ensure that only appropriate drawing packages are used and are in good condition when designing rigid PCBS.
The electrical components of a rigid PCB can be gathered in one place so that the PCB can be designed easily.
When placing components on rigid circuit boards, be sure to leave enough space between these components so as not to create a confusing and cumbersome design.
The polarized part of the rigid PCB is arranged in the same direction.
Maintain adequate clearance between the edges and components of the rigid PCB.
Place the heavy components of the rigid PCB on the main side of the board.
The elements should be designed in such a way that they can be welded by hand or assembled automatically according to the dimensions of the rigid PCB.
Advantages and disadvantages of printed circuit boards
Printed circuit boards (PCBS) are the basis for supporting and connecting surface mount and socket components in a variety of electronic products. In fact, most electronics use PCBS because of their many advantages. There are some drawbacks to using printed circuit boards. If you're not sure if PCBS are right for your electronics, let's explore the pros and cons to help you get a better idea of what's needed.
Advantages of printed circuit boards
l Complex wiring is not a problem: PCB design requires very little complex wiring on the board. With automated production equipment, the surface of the circuit board can be etched with the correct electronic circuit.
Better quality control: After designing and developing the board, testing becomes a breeze. You can perform quality control tests throughout the production cycle to ensure that your board is ready for use after the manufacturing process is complete.
Easy maintenance: Since the PCB's components are fixed in place, only limited maintenance is required. There are no loose parts or complex wiring (as described above), so it is easy to identify different parts and maintain them.
l The possibility of short circuit is very small: PCBS are almost immune to short circuit by relying on the embedded copper trace. Also, wiring errors are minimized, and circuit breaks are rare. Also, you'll be doing quality control testing, so if anything does go wrong, you can stop it in their tracks.
Disadvantages of printed circuit boards
l Single-use board: Printed circuit boards are designed with single-use in mind. If you want to modify the board after printing, you will not be able to, and you will need to create a new board from scratch. However, if you need to create a new board to replace the one that needs to be modified, the lower manufacturing costs may work in your favor.
l Etching is not an eco-friendly process: the chemicals used in etching can have a negative impact on the environment. Although the etching process is great for plates, it's not so great for planets.
l Compatibility: When designing PCBS, you must keep in mind that they are not compatible with every electronic device. Before you start building a circuit board, you need to determine the device you want to design for it.
What are the characteristics of special solder resistance for printed circuit boards
Resistance welding flux is printed printed circuit board components coated in the printing plate, its main function is to prevent the wave welding process in the "line" and short circuit, to protect the printed circuit board permanent. In addition, the printing plant can also save solder, reduce the weight of the printed circuit board, reduce the cost.
Solder resistance has the following properties: high temperature resistance, brazing temperature (260±2℃), in the specified welding time (5±2), no softening, no damage; Good electrical performance, surface insulation resistance should be greater than 1×10^ (3). Alcohol, acetone, banana water and other solvents. Has certain wear resistance, in the printing plate and other machine processing. Solder film should not be damaged. The colors are beautiful and even.
It can be divided into two types according to curing conditions: hot solid type and light solid type, hot solid type resistance flux, one component and two component. Single component modified epoxy resin, alkyd resin, amino resin, acrylic resin, polyurethane resin, melamine resin, silicone, epoxy resin as the main raw materials, adding appropriate amount of pigment, filler, curing agent, solvent, auxiliary materials, through grinding processing.
Two-component thermosetting flux is a hardener of imidazole or amine, that is, solidified solid or liquid epoxy resin. Uv curable flux is a kind of flux resistance commonly used in printing plants. Its main components are: light solid resin, photosensitizer, diluent, pigment, levelling agent and thixotropic agent.
photosolid resin is mainly composed of epoxy resin acrylate and its modifier, diluent and photosensitizer, mainly polyacrylate, general benzene ether. The characteristic of this solder resistance is UV irradiation in a certain wavelength range, and the cross-linking reaction can quickly cure the film. Usually does not contain volatile solvent, low temperature fast curing, can meet the requirements of mass production automation, high production efficiency, good product quality, heat resistant curing flux accounts for more than ten energy.