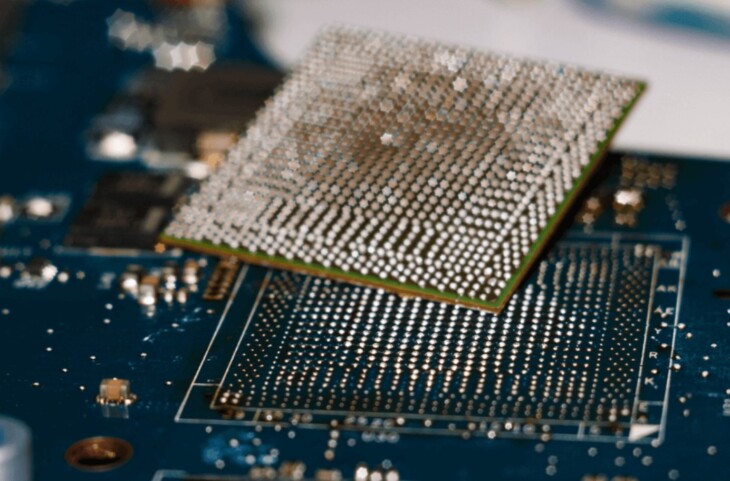
PCB multi-layer board design suggestions and examples (4,6,8,10,12 layers of board) description
A, the component surface, welding surface is a complete ground plane (shielding);
B, no adjacent parallel wiring layer;
C. All signal layers are adjacent to the ground plane as far as possible;
D, the hub signal is adjacent to the formation, and does not cross the division area.
Scheme 1: There is a ground plane under the component surface, and the hub signal is preferentially distributed in the TOP layer; As for the layer thickness setting, there are the following recommendations:
1, content impedance control
2, the core board (GND to POWER) should not be too thick to reduce the distributed impedance of the power supply and ground plane; Ensure the decoupling effect of the power plane.

Option 2: Defects
1. The distance between the power supply and the ground is too far, and the power plane impedance is too large
2. The power supply and ground plane are very incomplete because of the influence of the component pad
3, because the reference surface is incomplete, the signal impedance is discontinuous
Option 3:
Similar to scheme 1, it is used when the main device is laid out at the BOTTOM or the hub signal is wired at the bottom.
Scheme 4: A signal layer is reduced and an internal electrical layer is added, although the level available for wiring is reduced, but the scheme solves the defects common to scheme 1 and scheme 2.
Strengths:
1. The power layer and ground layer are tightly coupled.
2, each signal layer is directly adjacent to the internal electrical layer, and is effectively isolated from other signal layers, which is not easy to crosstalk.
3, Siganl_2 (Inner_2) and the two internal electrical layers GND (Inner_1) and POWER (Inner_3) adjacent, can be used to transmit high-speed signals. The two internal electric layers can effectively shield the interference of Siganl_2 (Inner_2) layer and Siganl_2 (Inner_2) layer from the outside world.
Scheme 5:4 signal layers and 2 internal power/ground layers are used, with more signal layers, which is conducive to the wiring work between components.
Defects:
1. The power layer and ground layer are separated far away and are not fully coupled.
2, the signal layer Siganl_2 (Inner_2) and Siganl_3 (Inner_3) are directly adjacent, the signal isolation is not good, and crosstalk is easily generated.
3 Shallow pits appear on the surface of the substrate or there are holes and foreign inclusions in the inner layer of the multi-layer plate
(1) Copper foil memory has copper nodules or resin protrusions and foreign particles superimposed. Solution: Raw material problem, need to propose to the supplier replacement.
(2) After etching, it was found that the surface of the substrate was transparent, and the slice was hollow. Solution: The same as the above method to solve.
(3) In particular, the thin substrate after etching has black spots that are particle states. Solution: Handle according to the above method.
4 Common defects on the copper surface of the substrate
(1) The copper foil has concave spots or pits, which is due to the existence of foreign impurities on the surface of the tool used in lamination. Solution: Improve the lamination and pressing environment to meet the cleanliness index requirements.
(2) The appearance of concave spots and glue spots on the surface of copper foil is due to the direct influence of foreign impurities during the pressing and laminating of the pressure plate mold used. Solution: Carefully check the surface state of the mold, improve the working environment between laminates and presses to meet the process requirements.
(3) In the manufacturing process, the tools used are not suitable for causing the poor condition of the copper foil surface. Solution: Improve the operation method and choose the appropriate process method.
(4) The copper foil on the surface of the pressed multilayer plate is creased because the laminated layer slips and flows improperly during pressing. Solution: When stacking, pay special attention to the accuracy of the position between the layers to avoid sliding during the feeding of the press. The stainless steel plate directly in contact with the surface of the copper foil should be placed with special care and kept flat.
(5) There are glue spots on the surface of the substrate, which may be caused by the rubber chips falling on the surface of the steel plate or the copper surface during the lamination. Solution: In order to prevent the rubber chip from falling off, the edge of the semi-cured sheet can be heat-sealed.
(6) There are pinholes on the surface of copper foil resulting in the overflow of molten glue during pressing. Solution: First of all, backlight inspection of the copper foil entering the factory must be strictly kept after passing, to avoid creases or tears.
5 White spots or white spots appear in the plate
(1) The plate withstands the impact of inappropriate mechanical external forces resulting in the separation of local resin and glass fiber into white spots. Solution: Take measures from the process to minimize or reduce the excessive vibration phenomenon of mechanical processing to reduce the role of external mechanical force.
(2) The local plate is infiltrated by fluorine-containing chemicals, and the erosion of the glass fiber fabric fabric points forms regular white spots (which can be seen to be square when more serious). Solution: Especially in the detinning lead alloy coating, it is easy to occur between the gold-plated plug and the plug, and attention should be paid to choosing the appropriate detinning lead solution and operation process.
(3) Improper thermal stress on the plate will also cause white spots and white spots. Solution: Especially hot air leveling, infrared hot melt, etc., such as control failure, will cause the effect of thermal stress resulting in defects in the substrate.