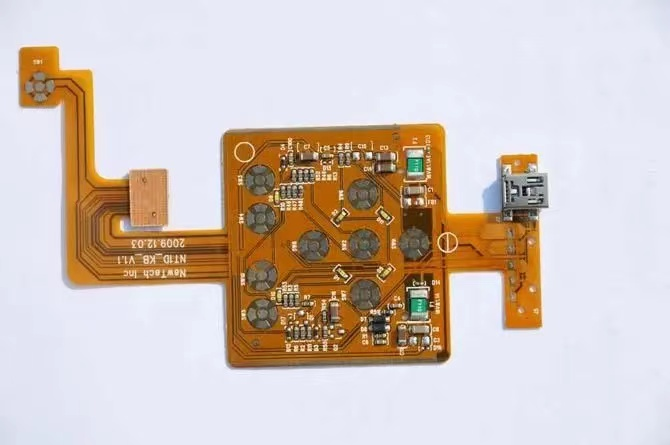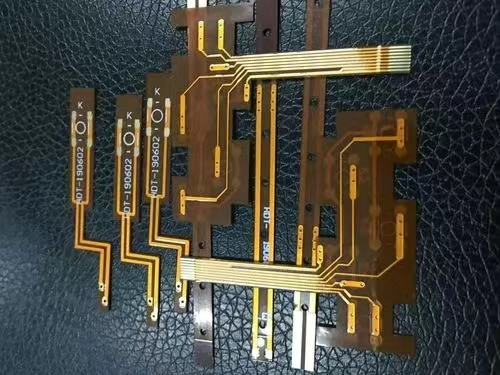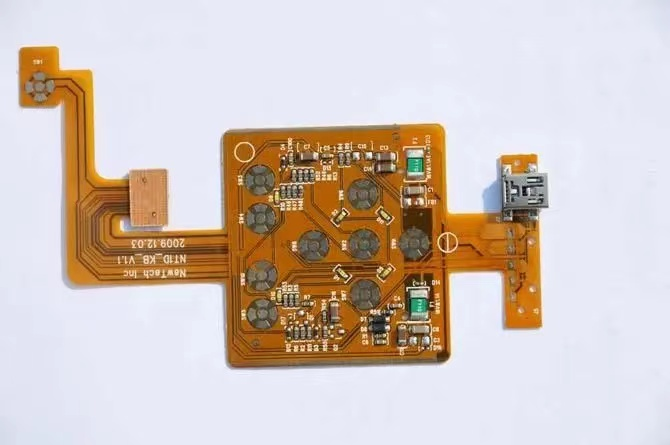
FPC cutting - double-sided FPC manufacturing process
Except for some materials, the materials used for flexible printed boards are basically coiled. As not all processes must be processed by tape rolling process, some processes must be cut into sheets for processing, such as the drilling of metallized holes on double-sided flexible printed boards, which can only be drilled in sheet form at present, so the first process of double-sided flexible printed boards is cutting.
The bearing capacity of flexible copper clad laminate to external forces is very poor, and it is easy to be injured. If the material is damaged during opening, the qualification rate of subsequent processes will be seriously affected. Therefore, in order to ensure the quality of materials, enough attention must be paid to even the seemingly simple materials. If the quantity is relatively small, manual shears or hob cutters can be used, and automatic shears can be used for large quantities.
Whether it is single-sided, double-sided copper foil laminate or covering film, the precision of the cut size can reach ± O 33。 The reliability of material opening is high. The opened materials are automatically stacked neatly. No personnel are required to receive materials at the exit. The damage to the material can be controlled to the minimum. With the change of the size of the feeding roller, the material has almost no wrinkles and scars. In addition, the latest device can also automatically cut the flexible printed circuit board etched by the tape rolling process. The optical sensor can detect the corrosion positioning pattern and conduct automatic blanking positioning. The blanking accuracy is up to 0.3 mm, but this blanking frame cannot be used as the positioning of the subsequent process.
FPC drilling through hole - double-sided FPC manufacturing process
The through hole of flexible printed circuit board can also be drilled by numerical control just like that of rigid printed circuit board, but it is not applicable to the hole processing of double side metallized hole circuit of tape rolling. With the high density of circuit graphics and the small aperture of metallized holes, and the aperture of CNC drilling has a certain limit, many new drilling technologies have been applied in practice. These new drilling technologies include plasma etching, laser drilling, micro hole punching, chemical etching, etc. These drilling technologies are easier to meet the requirements of tape rolling process than NC drilling.
The through hole of flexible printed circuit board can also be drilled by numerical control just like that of rigid printed circuit board, but it is not applicable to the hole processing of double side metallized hole circuit of tape rolling. With the high density of circuit graphics and the small aperture of metallized holes, and the aperture of CNC drilling has a certain limit, many new drilling technologies have been applied in practice. These new drilling technologies include plasma etching, laser drilling, micro hole punching, chemical etching, etc. These drilling technologies are easier to meet the requirements of tape rolling process than NC drilling.
1. CNC drilling
Most of the holes drilled in the double-sided flexible printed circuit board are still drilled by the numerical control drilling machine. The numerical control drilling machine is basically the same as the numerical control drilling machine used in the rigid printed circuit board, but the drilling conditions are different. Because the flexible printed circuit board is very thin, multiple pieces can be overlapped for drilling. If the drilling conditions are good, 10~15 pieces can be overlapped for drilling. Paper based phenolic laminate or glass fiber cloth epoxy laminate can be used for base plate and cover plate, or aluminum plate with thickness of 0.2~0.4 mm can be used completely. Drill bits for flexible printed boards are available in the market. Drill bits for drilling rigid printed boards and milling cutters can also be used for flexible printed boards.
The processing conditions for drilling, milling the covering film and the shape of the reinforcing plate are basically the same, but because the adhesive used for the flexible printed board material is soft, it is very easy to attach to the drill bit, so the drill bit status needs to be checked frequently, and the rotation speed of the drill bit should be properly increased. The drilling of multilayer flexible printed boards or multilayer rigid flexible printed boards shall be particularly careful.
2. Punching
Punching small aperture is not a new technology, and has been used in mass production. As the coiling process is continuous production, there are also many examples of using punching to process the through-hole of the coiling. However, the batch punching technology is limited to punching holes with a diameter of 0.6~0.8mm. Compared with the NC drilling machine, the processing cycle is long and requires manual operation. Because the size of the initial process is large, the punching mold is correspondingly large, so the mold price is expensive. Although mass production is beneficial to reducing costs, the equipment depreciation burden is large, and small batch production and flexibility cannot compete with the NC drilling, So it is still not universal.
However, in recent years, great progress has been made in both die precision and NC drilling of punching technology, and the practical application of punching technology in flexible PCB has been very feasible. The latest die manufacturing technology can make holes with a diameter of 75 um that can be punched into the adhesive free copper clad laminate with a base material thickness of 25 um. The reliability of punching is also quite high. If the punching conditions are suitable, even holes with a diameter of 50 um can be punched. The punching device has also been numerically controlled, and the mold can also be miniaturized, so it can be well applied to the punching of flexible printed boards. NC drilling and punching cannot be used for blind hole processing.
3. Laser drilling
The laser can be used to drill the smallest through hole. The laser drilling machines used to drill through holes on flexible printed boards include excimer laser drilling machines, impact CO2 laser drilling machines, YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) laser drilling machines, argon laser drilling machines, etc.
The impact CO2 laser drill can only drill holes on the insulating layer of the substrate, while the YAG laser drill can drill holes on the insulating layer and copper foil of the substrate. The speed of drilling the insulating layer is obviously faster than that of drilling copper foil. It is impossible to use the same laser drill to drill all the holes. Generally, the copper foil is etched first to form a hole pattern, and then the insulating layer is removed to form a through-hole, so that the laser can drill holes with extremely small aperture. However, the position accuracy of upper and lower holes may restrict the hole diameter. If the blind hole is drilled, as long as the copper foil on one side is etched off, there is no problem of up and down position accuracy. This process is similar to the plasma etching and chemical etching described below.
At present, the hole processed by excimer laser is the most fine. Stimulated excimer laser is ultraviolet ray, which directly damages the structure of the resin in the base layer, making the resin molecules discrete and generating very little heat. Therefore, the damage degree of heat around the hole can be limited to the minimum range, and the hole wall is smooth and vertical. If the laser beam can be further reduced, holes with a diameter of 10-20um can be processed. Of course, the greater the thickness aperture ratio, the more difficult it is to wet copper plating. The problem of excimer laser drilling is that the decomposition of polymer will produce carbon black attached to the hole wall, so some means must be taken to clean the surface before electroplating to remove carbon black. However, when laser processing blind holes, the uniformity of the laser also has some problems, which will produce bamboo like residues.
The biggest difficulty of excimer laser is that the drilling speed is slow and the processing cost is too high. Therefore, it is limited to the machining of high-precision and highly reliable micro holes.
Shock CO2 laser generally uses CO2 gas as the laser source and radiates infrared ray. Unlike the excited excimer laser, which burns and decomposes resin molecules due to thermal effect, it belongs to thermal decomposition. The shape of the processed hole is much worse than that of the excited excimer laser, and the hole diameter that can be processed is basically 70~100um, but the processing speed is significantly faster than that of the excited excimer laser, and the cost of drilling is much lower. Even so, it is still much more expensive than the plasma etching method and chemical etching method described below, especially when there are many holes per unit area.
It should be noted that the impact CO2 laser can only be emitted to the surface of copper foil when processing blind holes, and it is not necessary to remove the organic matters on the surface. In order to stably clean the copper surface, chemical etching or plasma etching should be used as post-treatment. Considering the technical possibility, the laser drilling process is basically not difficult to be used in the tape rolling process. However, considering the balance of processes and the proportion of equipment investment, it does not have an advantage. However, the TAB (Tape Automated Bonding) is narrow in width, and the tape rolling process can improve the drilling speed. There have been practical examples in this regard.
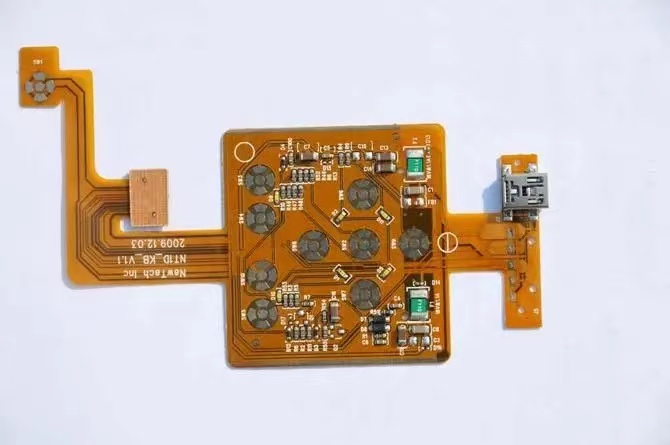
Product Diagram of FPC Manufacturing Process for Double sided Flexible Circuit Board
Hole metallization - double-sided FPC manufacturing process
Hole metallization of flexible printed boards is basically the same as that of rigid printed boards.
In recent years, a direct electroplating process using the technology of forming carbon conductive layer instead of electroless plating has emerged. Hole metallization of flexible printed boards also introduces this technology.
Due to the softness of flexible printed boards, special fixture is required. The fixture can not only fix the flexible printed boards, but also must be stable in the plating solution. Otherwise, the copper plating thickness is uneven, which is also an important reason for wire breakage and bridging in the etching process. In order to obtain a uniform copper coating, the flexible printed circuit board must be tightened in the fixture, and efforts must be made on the position and shape of the electrode.
For hole metallization outsourcing processing, try to avoid outsourcing to factories without experience in flexible PCB hole forming. If there is no special electroplating line for flexible PCB, the hole forming quality cannot be guaranteed.
Cleaning of copper foil surface - FPC manufacturing process
In order to improve the adhesion of the resist mask, the copper foil surface should be cleaned before the resist mask is coated. Even such a simple process requires special attention for flexible printed boards.
General cleaning includes chemical cleaning process and mechanical grinding process. When manufacturing precision graphics, the two kinds of cleaning processes are combined for surface treatment in most cases. Mechanical grinding uses brush polishing method. If the brush polishing material is too hard, it will damage the copper foil. If it is too soft, it will not be fully ground. Generally, nylon brush is used, and the length and hardness of the brush must be carefully studied. Use two brush throwing rollers and place them on the conveyor belt. The rotation direction is opposite to the belt transmission direction. However, if the pressure of the brush throwing roller is too large at this time, the substrate will be stretched under great tension, which is one of the important reasons for size change.
If the copper foil surface is not cleaned, the adhesion to the resist mask will be poor, which will reduce the qualification rate of the etching process. Recently, due to the improvement of the quality of copper foil, the surface cleaning process can also be omitted in the case of single-sided circuits. But OO μ Surface cleaning is an essential process for precision graphics below m.
Coating of resist - double-sided FPC manufacturing process Now, the coating method of resist can be divided into the following three methods according to the precision and output of circuit graphics: screen printing method, dry film/photosensitive method, and liquid resist photosensitive method.
At present, the coating methods of resist are divided into the following three methods according to the precision and output of circuit graphics: screen leak printing method, dry film/photosensitive method, and liquid resist photosensitive method.
The anti-corrosive ink uses the screen leak printing method to directly leak print the line graphics on the copper foil surface, which is the most commonly used technology, suitable for mass production, and low cost. The precision of the formed line graph can reach 0.2~0.3 mm of line width/spacing, but it is not suitable for more precise graphs. This method can not be adapted gradually with the micronization. Compared with the dry film method described below, it requires technicians to operate , and the operators must be trained for many years, which is an unfavorable factor.
The dry film method can produce 70~80 as long as the equipment and conditions are complete μ M line width figure. At present, most of the precision patterns below 0.3mm can be formed into corrosion resistant line patterns by dry film method. Dry film with thickness of 15-25 μ m. If possible, the batch level can be 30~40 μ The figure of m line width.
When selecting the dry film, it must be determined according to the matching with the copper foil and the process and through tests. Even if the experimental level has good resolution, it may not have a high qualification rate in mass production. Flexible printed boards are thin and easy to bend. If a hard dry film is selected, it will be brittle and have poor mobility, so cracks or peeling will occur, thus reducing the qualification rate of etching.
The dry film is rolled, and the production equipment and operation are relatively simple. The dry film is composed of a thin polyester protective film, a photoresist film and a thick polyester release film. Before pasting the film, first peel off the release film (also called the diaphragm), and then stick it on the surface of the copper foil with a hot roller. Before developing, tear off the protective film (also called the carrier film or the covering film) on it. Generally, there are guide positioning holes on both sides of the flexible printed board, and the dry film can be slightly narrower than the flexible copper foil to be pasted. The automatic film pasting device for rigid printed boards is not applicable to the film pasting of flexible printed boards, and some design changes must be made. Due to the high linear speed of dry film pasting compared with other processes, many factories do not use automatic pasting, but use manual pasting.
After pasting the dry film, in order to make it stable, it should be exposed after 15~20min.
If the line width of line graph is 30 μ Below m, if the figure is formed by dry film, the qualification rate will decrease significantly. Generally, liquid photoresist is used instead of dry film in batch production. The coating thickness will vary with different coating conditions. If the coating thickness is 5~15 μ M of liquid photoresist at 5 μ On m thick copper foil, the laboratory level can etch 10 μ Line width below m.
The liquid photoresist must be dried and baked after coating. Because this heat treatment will have a great impact on the performance of the photoresist film, the drying conditions must be strictly controlled.
The above is the complete solution of FPC manufacturing process for double-sided flexible circuit board