Printed circuit boards or PCBs are key components of electronic components. Most people use them every day without even thinking about it, and they are vital to all walks of life. There are tons of applications for PCBs, but we'll cover 10 of the most common printed circuit board uses.
What is a printed circuit board used for?
A PCB is a board that connects electronic components. They are an integral part of the electronic products we use in our daily lives in all walks of life. They are made of non-conductive material and have traces, pads and other features etched from copper sheets to electrically connect electronic components within the product. Components like capacitors and resistors are also soldered to some PCBs.
Today, PCBs are widely used in electronic products and there are various types of PCBs. They can be single-sided, double-sided or multi-layered. They can be rigid, flexible or contain both rigid and flexible components.
Type of Assembly Process
There are two main methods for PCB applications - through hole and surface mount.

1. Through-hole mounting
During through-hole mounting, the assembler places component leads in holes drilled in the bare PCB. This technology was originally used for PCBs.
Through-hole technology produces stronger connections than surface mount technology, so it is used in applications that require high reliability. This is because the leads go all the way through the board instead of being connected with solder like surface mount. Through-hole technology is also useful for testing and prototyping applications that require manual adjustment of components.
2. Surface Mount
In the surface mount process, components are mounted directly to the surface of the PCB using solder. This method was developed in the 1960s and became popular in the 1980s. Today, it is the most commonly used component mounting method. Instead of through-hole components, surface mount boards use small components called through-holes to connect the various layers of the PCB.
Using surface mount allows assemblers to attach components to both sides of the board. Surface mount components can also be smaller, allowing more parts to fit on a board. This has lowered costs and has allowed electronic devices to get smaller and smaller over the years. Surface mounts can also be done faster and involve fewer processes than through-hole mounts, further reducing costs.
What are the common uses of PCBs?
Because PCBs are used in many different industries, you can find them almost anywhere, from small consumer devices to large machinery. Where are printed circuit boards used? Below are the 10 most common PCB applications by industry.
1. Medical Devices
As technology advances, more and more PCBs are being used in the healthcare industry, showing new capabilities. PCBs play an important role in devices used for diagnosis, monitoring, therapy, and more.
Special care must be taken to ensure reliability when producing medical PCBs, as proper operation is critical to patient health. In many cases, PCBs must also meet stringent hygiene standards, especially for implants. Plates for implants and many other applications, such as emergency room monitors, must also be relatively small. Because of this, many medical PCBs are high-density interconnects or HDIs.
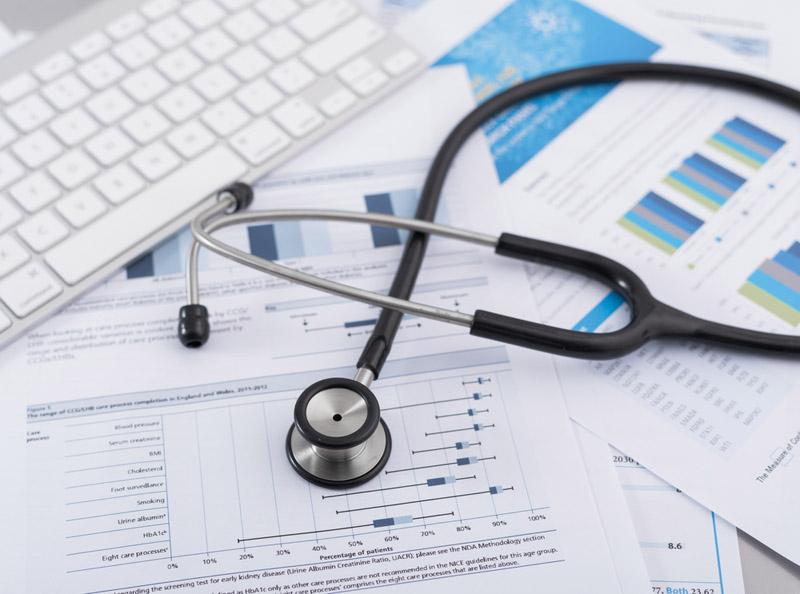

PCBs are used in medical devices such as:
Medical Imaging Systems: CT, CAT, and ultrasound scanners often use PCBs, as do the computers that compile and analyze these images.
Monitors: Heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar monitors, etc. rely on electronics to get accurate readings.
Infusion pumps: Infusion pumps, such as insulin and patient-controlled analgesia pumps, deliver precise amounts of fluid to patients. PCBs help ensure that these products operate reliably and accurately.
Internal Devices: Pacemakers and other devices used internally require small PCBs to function.
The medical industry continues to provide more uses for electronics. As technology advances and smaller, denser, more reliable circuit boards become possible, PCBs will play an increasingly important role in healthcare.
2. Light Emitting Diodes
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are an increasingly popular lighting technology used in residential and commercial lighting and in numerous industries including automotive, medical and computer technology. LEDs are favored for their energy efficiency, long life and compactness.
One of the roles of the PCB in LED applications is to transfer heat away from the bulb. High temperatures reduce the average lifespan of LEDs. Therefore, PCBs used for LEDs are usually made of aluminum, which transfers heat better than other metals. This eliminates the need for an extra heat sink for the design and means it can be more compact.
You can find LED PCBs at:
Residential Lighting: LED lighting, including smart light bulbs, helps homeowners light their properties more efficiently.
Storefront Lighting: Businesses can use LEDs to sign and illuminate their stores.
Automotive Displays: Dashboard indicators, headlights, brake lights, etc. may use LED PCBs.
Computer Monitors: LED PCBs power many indicators and displays on laptop and desktop computers.
Medical Lighting: LEDs provide bright light and emit very little heat, making them ideal for medical applications, especially those related to surgery and emergency medicine.
LEDs are becoming more common in a variety of applications, which means that PCBs are likely to continue to play a more prominent role in lighting.
3. Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, computers, and many other consumer products that people use every day require PCBs to function. As we add electronics to more products, PCBs have become an essential part of our daily lives.
Manufacturers are producing smaller and smaller smartphones and laptops that still have many advanced features that require small PCBs with lots of connections. PCBs used in consumer electronics also need to be relatively low cost to keep the price of the final product low. Manufacturers also need reliable circuit boards because they need their products to perform as expected in order to stay in business.
A large number of consumer products use PCBs, including:
Communication Devices: Smartphones, tablets, smart watches, radios, and other communication products require PCBs to function.
Computers: Computers for personal and business use have PCBs.
Entertainment Systems: Entertainment-related products such as TVs, stereos, and video game consoles all rely on PCBs.
Home Appliances: Many home appliances also have electronic components and PCBs, including refrigerators, microwaves, and coffee makers.
The use of PCBs in consumer products is certainly not slowing down. The percentage of Americans now owning a smartphone is 77% and growing. Meter
Any device that was not electronic before now also gains advanced electronic capabilities and is part of the Internet of Things (IoT).
4. Industrial equipment
The uses of printed circuit boards in industry vary widely. Electronic components power much of the equipment in manufacturing and distribution centers and other types of industrial facilities.
PCBs used in the industrial sector often require particularly high power and are durable enough to withstand the harsh conditions that exist in industrial facilities. PCBs may need to withstand rough handling, vibrating machinery, extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals. To meet this need for durability, industrial PCBs can be made of durable metals or heat-resistant materials and be thicker than other types of PCBs. Industrial PCB assembly services may include through-hole technology for improved durability.
Some industrial applications of PCBs include:
Manufacturing Equipment: PCB-based electronic power drills and presses for manufacturing.
Power Equipment: Components that power a wide variety of industrial equipment use PCBs. The power equipment includes DC to AC power inverters, solar cogeneration equipment, etc.
Measuring Devices: PCBs often power devices that measure and control pressure, temperature, and other factors.
As robotics, industrial IoT technology, and other types of advanced technologies become more commonplace, new uses for PCBs are emerging in industry.
5. Auto parts
Automakers are using more and more electronic components in their vehicles. In the early days, PCBs were only used for things like windshield wipers and headlight switches, but today they implement many advanced features that make driving safer and easier.
Depending on which part of the car the PCB is used in, it may need to be able to withstand extreme temperatures or vibrations. When it comes to the safety features of the car, their reliability is also important. Because of these challenges, manufacturers may use high temperature laminates, aluminum or copper substrates, or through-hole mount components. They also use rigid-flex PCBs because they can withstand vibration.
Today, you can find PCBs in automotive components such as:
Entertainment and Navigation Systems: Stereo systems and systems that integrate navigation and entertainment rely on PCBs.
Control Systems: Many systems that control the basic functions of the car rely on electronics powered by the PCB. These include the engine management system and fuel regulator.
Sensors: As cars become more advanced, manufacturers are incorporating more and more sensors. These sensors can monitor blind spots and warn drivers of nearby objects. The PCB is also required for the system that enables the car to automatically parallel park.
These sensors are part of what enables the car to drive itself. Fully autonomous vehicles are expected to become common in the future, which is why a large number of printed circuit boards are used.
6. Aerospace Components
Electronics used in aerospace applications have similar requirements to those used in the automotive industry, but aerospace PCBs may be exposed to harsher conditions. PCBs are used in a variety of aerospace equipment, including aircraft, space shuttles, satellites, and radio communication systems.
Aerospace PCB manufacturing requires the use of materials that can withstand large amounts of vibration, extreme temperatures, and other harsh conditions. Some aerospace PCBs even need to be able to operate in outer space and must be very durable. Plates made from lightweight materials such as aluminum are also beneficial for aerospace. Anodized aluminum can be used to increase oxidation resistance.
Some uses of PCBs in aerospace include:
Power: PCBs are key components in equipment that power a variety of aircraft, control towers, satellites, and other systems.
Monitoring Equipment: Pilots use a variety of monitoring equipment, including accelerometers and pressure sensors, to monitor the functions of the aircraft. These displays usually use a PCB.
Communication Equipment: Communication with ground control is an important part of ensuring the safety of air travel. These critical systems depend on the PCB.
7. Maritime applications
Various ships and systems rely on PCBs to function. This includes small boats, large cargo ships, submarines, communication systems and navigation equipment.
PCBs for offshore applications must also be able to withstand harsh conditions. Maritime PCB manufacturers emphasize reliability, as proper functioning of electronic equipment is critical to the safety of crew and passengers.
Navigation Systems: Many marine vessels rely on PCBs for their navigation systems. You can find PCBs in GPS and radar systems and other equipment.
Communication System: The radio system used by the crew to communicate with the port and other ships requires the PCB.
Control Systems: Many control systems on marine vessels, including engine management systems, power distribution systems, and autopilot systems, use PCBs. These autopilot systems may help the vessel stabilize, maneuver, minimize heading errors and manage rudder activity.
8. Security equipment
Many aspects of security systems, whether in homes, businesses or government buildings, rely on PCBs. They play a more role in our safety and security than many realize.
The ideal type of PCB depends on its specific application, but all PCBs used in safety and security applications need to be reliable because these products must always perform as intended to be effective. Some safety equipment may be used outdoors and a PCB that can withstand the outdoor environment should be used.
Some safety and security devices that use PCBs include:
Security Cameras: Security cameras, whether used indoors or outdoors, rely on PCBs, as do the devices used to monitor security footage.
Smoke Detectors: Smoke detectors and other similar devices such as carbon monoxide detectors require a reliable PCB to function.
Electronic Door Locks: Modern electronic door locks also contain PCBs.
Motion Sensors and Burglar Alarms: Security sensors that detect motion also rely on PCBs.
PCBs play an important role in many different types of security devices, especially as more and more of these products are able to connect to the Internet.
9. Telecommunications equipment
PCBs are an important part of the telecommunications industry. They are necessary for consumer devices like smartphones and the infrastructure that makes them work.
Due to the wide variety of equipment used in the industry, the telecommunications industry uses a wide variety of PCBs. Some equipment remains in a stable indoor environment, while some infrastructure must be able to withstand outdoor conditions including storms and extreme temperatures.
The following telecommunications equipment requires a PCB:
Telecom Towers: Cell towers receive and transmit signals from cell phones and require PCBs that can withstand outdoor environments.
Office Communications Equipment: PCBs are required for many communications equipment you may find in the office, including telephone switching systems, modems, routers, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) equipment.
LED Displays and Indicators: Telecommunications equipment often includes LED displays and indicators using PCBs.
The telecommunications industry is constantly evolving, and so are the PCBs used in the industry. As we generate and transmit more data, powerful PCBs will become more important for communication.
10. Military and Defense Applications
The military uses PCBs for a wide range of applications, including communications equipment, computers, vehicles, firearms, and more.
PCBs used in military applications must be very reliable and durable. They may be exposed to extreme conditions and may play a role in national security. The military uses materials such as high temperature laminates, aluminum and copper because of their ability to withstand harsh conditions such as high temperatures. Anodized aluminum can be used because of its resistance to oxidation. Some military printed circuit board applications may also benefit from the enhanced reliability of through-hole technology.
Some military and defense uses of PCBs include:
Communication Equipment: Radio communication systems and other critical communications require PCBs to function.
Control system: PCB is the core of various equipment control systems, including radar jamming systems, missile detection systems, etc.
Instrumentation: PCBs enable members of the military to use indicators to monitor threats, conduct military operations, and operate equipment.
The military is often at the forefront of technology, so some of the most advanced uses of PCBs are for military and defense applications. The use of PCBs in the military varies widely.