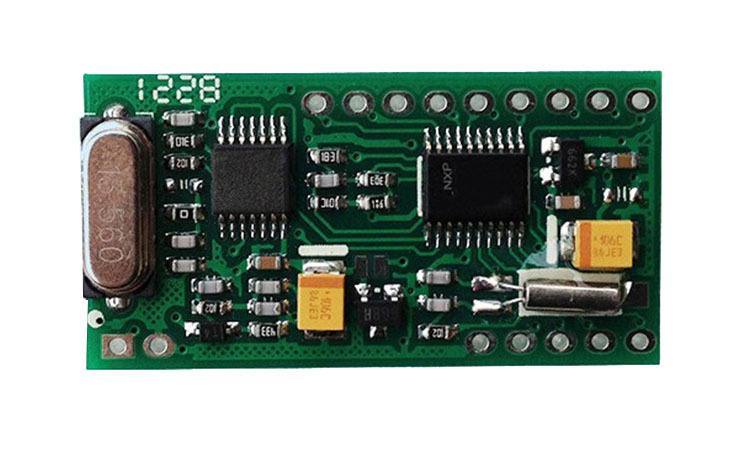
High frequency printed circuit boards are used to transmit electromagnetic waves of GHz frequency with minimal loss. Therefore, printed circuit boards with certain characteristics are used to transmit these electromagnetic waves. There are several parameters to consider when designing PCBS for high frequency applications. This article discusses these factors, as well as the application of high frequency printed circuit boards.
Factors affecting the design of high frequency PCB
The following describes some of the factors required to design a high frequency PCB:
● PCB material selection for high speed digital circuits is affected by several factors. High frequency PCBS must provide the following functions in addition to good construction. Impedance controlled multilayer
● Sandwich accumulation for material combination
● Controlled production line
● Signal loss tolerance
● Heat dissipation capacity
● Operating temperature (temperature expansion, stability in the temperature range)
● Production cost
Materials used to make high frequency PCB
The performance of high-frequency boards used in wireless or other high-frequency applications depends on the building material. In many applications, the use of FR4 materials with appropriate layering has improved dielectric properties. Some other materials for high frequency plates are listed below:
● Rogers 4350B HF
● ISOLA IS620 Electronic Fiber Glass
● Taconic RF-35 Ceramics
● Taconic TLX
● Rogers RO3001
● Rogers RO3003
● Yaron 85N
Application of high frequency PCB:
High frequency PCBS are used in the following applications:
● Automotive radar system
● Global Positioning satellite dish
Cellular telecommunications systems -- power amplifiers and antennas
● Live broadcasting satellite
E-band point-to-point microwave link
● Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags
● Airborne and ground radar systems
● Millimeter wave application
● Missile guidance system
● Space satellite transceiver
How to select suitable board materials for flexible PCB manufacturing?
Flexible or flexible printed circuit boards (PCBS) are one of the popular types of circuit boards that meet the needs of flexible electronic circuits. Designed to replace traditional wiring harnesses, flexible PCBS can be easily shaped to fit a variety of complex electronic designs. Moreover, these plates provide design freedom while maintaining density and performance. Although the performance of flexible PCBS depends on many factors, the main materials play a key role in them. Selecting the best material is critical to the success of flexible PCB components. Today, a wide variety of materials are available in different configurations to meet the needs of modern applications. This article focuses on the different aspects of materials used in the manufacture of flexible PCBS. So stay tuned for more information.
Flexible core or substrate materials commonly used in the manufacture of flexible PCB
Flexible circuit boards require adhesive and binder-free materials to attach their layers. Both materials offer a range of polyimide core thicknesses.
l Flexible adhesive material:
These types of materials are the main body of flexible circuit board materials. As the name suggests, they use acrylic or epoxy-based adhesives to attach copper glue to a flexible core. Some important advantages of viscous flexible cores include higher copper stripping strength, reduced material costs, and so on. Binder-based materials are commonly used in single-sided and double-sided flexible circuit board designs.
l Glueless flexible material:
As the name suggests, these types of flexible core materials have copper attached directly to the core without any adhesive. They can either cast a dielectric on copper or sputter copper on a dielectric film. Usually, they are preferred for flexible plates with a large number of layers. There are several reasons for the popularity of adhesive-free materials, including the elimination of bending thickness, improved flexibility, tighter minimum possible bending radius, potentially higher temperature ratings, improved controlled impedance signal characteristics, and more.
Flexible PCB conductor material
Copper is the most preferred and readily available conductor material for flexible PCB assembly. The material is used because of its beneficial properties, including good electrical characteristics, high machinability, etc. There are two types of bendable material configuration of copper foil: rolled annealing (abbreviated RA) and electrodeposition (abbreviated ED). These foils come in a variety of weights and thicknesses. Finish the foil before assembling the board. Combined with the relatively low cost, electrodeposited copper foil has become popular in the market. Unlike ED copper foil, RA is quite expensive but has enhanced features.
Flexible solder resistance material and overlay for flexible PCB manufacture
Flexible PCBS include cladding, solder resistance or a combination of the outer circuit. In the early days, Oems used adhesives to bond layers to the core. However, this method reduces the reliability of the circuit board. To solve this problem, they now prefer overlay layers due to their higher flexibility and reliability. Coverlay features a solid layer of polyimide with an epoxy resin or acrylic adhesive. Similarly, solder resistance layers are commonly used in rigid assembly areas with high density SMT components. Good design practices include using cladding in flexible areas and solder resistance in component areas to explore its functionality.