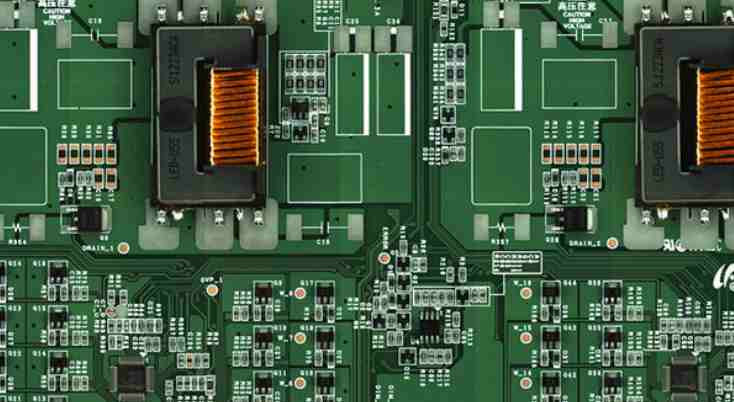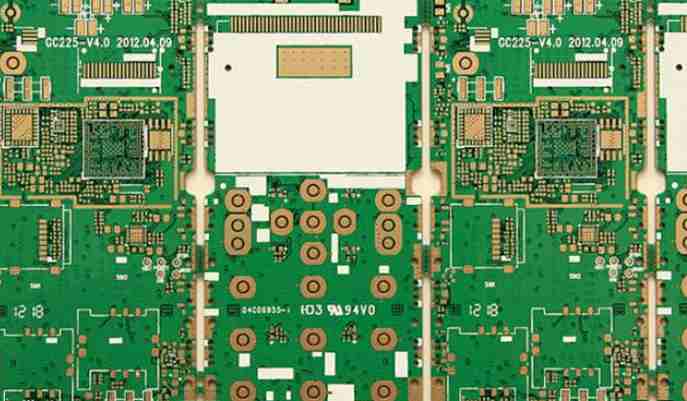
For PCB circuit board short circuit inspection method, Shenzhen Jieduobang Technology Co., Ltd. engineers give the following suggestions:
1. If it is manual welding, to develop a good habit, first of all, before welding to visually check the PCB board, and use a multimeter to check whether the key circuit (especially power and ground) short circuit; Secondly, after each welding of a chip, use a multimeter to test whether the power supply and ground short circuit; In addition, do not toss the soldering iron when welding, if the solder is thrown to the welding foot of the chip (especially the table sticker components), it is not easy to find.
2. Open the PCB diagram on the computer, light up the short-circuit network, and see where it is closest and most easily connected. Pay special attention to IC internal short circuit.
3. A short circuit is detected. Take a board to cut the line (especially suitable for single/double layer board), after the cut line will each part of the functional block power separately, part part of the exclusion.
4. Use short-circuit positioning analyzer, such as: Singapore PROTEQ CB2000 short-circuit tracker, Hong Kong Lingzhi Technology QT50 short-circuit tracker, UK POLAR ToneOhm950 multi-layer circuit short-circuit detector.
5. If there is a BGA chip, because all the solder joints are covered by the chip can not be seen, and it is a multilayer board (more than 4 layers), so it is best in the design of the power supply of each chip is divided, connected with magnetic beads or 0 ohl resistance, so that when there is a short circuit between the power supply and the ground, disconnect the magnetic bead detection, it is easy to locate a chip. Because of the difficulty of BGA welding, if the machine is not automatic welding, a little attention will be the adjacent power and the ground two welding ball short circuit.
6. Be careful when welding small size sticker capacitors, especially power filter capacitors (103 or 104), which can easily cause short circuit between power supply and ground. Of course, sometimes, unfortunately, the capacitor itself will be short-circuited, so the best way is to check the capacitor before welding.
Small batch PCB assembly: A testing ground for design
One example is circuit board development, where a team is often required to prove the design's accuracy. This is due to the fact that the process of demonstrating a successful PCB design consists of three stages: design, manufacture and testing. For boards of any complexity, development is a circular process that includes PCB prototype iterations. To a large extent, the efficiency of this process depends on how well you take advantage of the flexibility of board assembly. Before going into detail about the options available during prototyping, let's first define a small batch PCB assembly.
Small batch PCB assembly is defined
The manufacturing process of the printed circuit board consists of three parts. These are circuit board manufacturing, component procurement and PCB assembly. The optimization of these three manufacturing activities depends on the synchronization between the contract manufacturer (CM) and the equipment and processes used in the design. In fact, there is a direct proportional relationship between the quality of your PCB and the establishment of CM's DFM rules and guidelines. For production, small batch or large batch, strict adherence to DFM and DFA is to achieve the highest yield and lowest production cost.
Regardless of the level of development or production, the manufacture of the board is likely to remain the same unless a design change specifies otherwise. Assembly, on the other hand, may vary depending on whether you are prototyping (or perfecting a design) or producing a board to be delivered. In some cases, production may be small. For example, when manufacturing critical or specialized PCbas for aerospace, medical devices, industrial, automotive, or military purposes. However, as described below, small batch PCB assembly is an important part of all board development.
Small-lot PCB assembly is the installation of components on a relatively small number of bare boards, ranging from a few to 250 or less.
Assembly, although fundamentally defined in terms of steps, provides a great deal of flexibility, as described in the next section. If used properly, it can really improve your board development efficiency.
Validate your design using a small volume PCBA
For all board development, good PCB design elements should be brought forward. For assembly, in addition to sensible component placement decision, you should also know that can be used to help speed up the design verification of various options, often referred to as the prototype design or design ⇒ ⇒ test iteration process. These optionscan be classified as part of a sequential or parallel prototyping strategy.
Prototype options for small batch PCB assembly
l sequential
The most common approach in design validation is a sequential prototyping strategy that incorporates or tests a small number of design changes per cycle.
l parallel
Parallel prototyping can be used to reduce or minimize the number of production runs required. This is done by making multiple design changes to a small number of boards and then testing all variants before the next manufacturing run. These variants are for assembly only, and all bare plates are manufactured in a similar manner.
For both strategies, you can perform the following assembly options:
l Do not place (DNP)
In order to test a particular component or subcircuit, it is best not to place other components that may make testing and troubleshooting more complex and difficult.
l Use different variations
An extension of DNP is to place different sets of components on different boards to simplify testing.
l Use lead-based solder instead of lead-free solder
During prototyping, rework is often required and it is much easier to use lead-based solder than lead-free solder.
l Use a redo-able finish
Since rework may be required, it is best to use a surface finish that is easy to rework or not prototype at all.