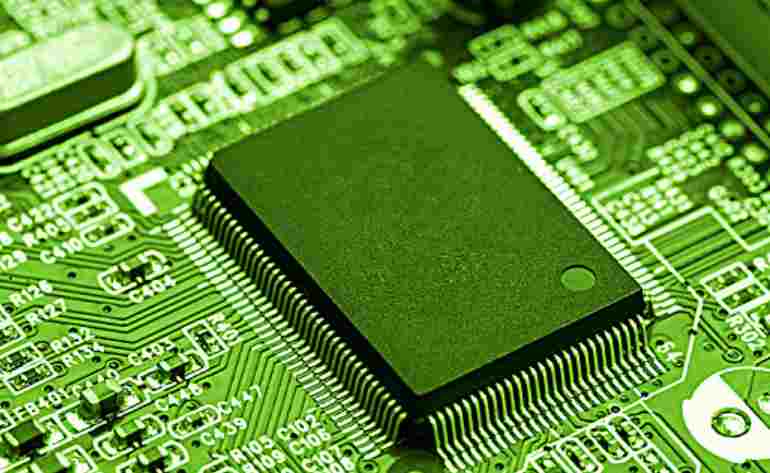
Ultraviolet laser is the best choice for a variety of PCB material applications in many industrial fields, from the production of the most basic circuit board, circuit wiring, to the production of pocket embedded chips and other advanced processes are common. This material difference makes the UV laser the best choice for a variety of PCB material applications in many industrial fields, from the production of the most basic circuit board, circuit wiring, to the production of pocket embedded chips and other advanced processes are common.
Application 1: Surface etching/Circuit production
Ultraviolet lasers work quickly to produce circuits, etching surface patterns onto circuit boards in minutes. This makes UV lasers the fastest way to produce PCB samples. R&d has noticed that more and more sample laboratories are being equipped with in-house UV laser systems.
Depending on the verification of optical instruments, the size of ultraviolet laser beam can reach 10-20μm to produce flexible circuit trace. The application in Figure 2 shows the greatest advantage of UV in producing circuit traces that are so tiny that they need to be seen under a microscope.
The board measures 0.75 "x0.5" and consists of a sintered ceramic substrate with a tungsten/nickel/copper/surface. The laser can produce circuit traces of 2mils, spaced 1 mil apart, making the entire spacing only 3 mils.
Although producing circuits using laser beams is the fastest method for PCB samples, large-scale surface etching applications are best left to chemical processes.
Application 2:PCB disassembly
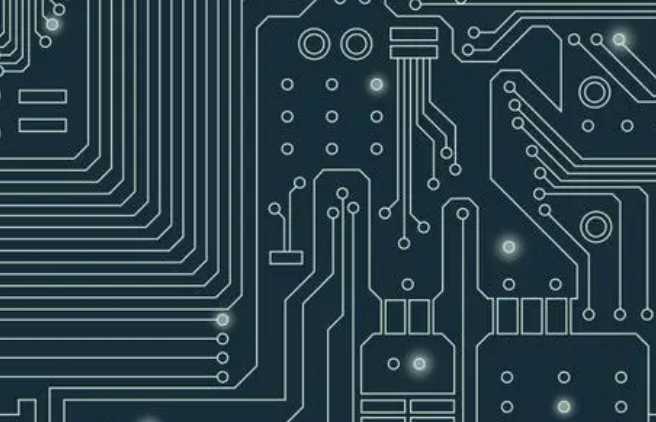
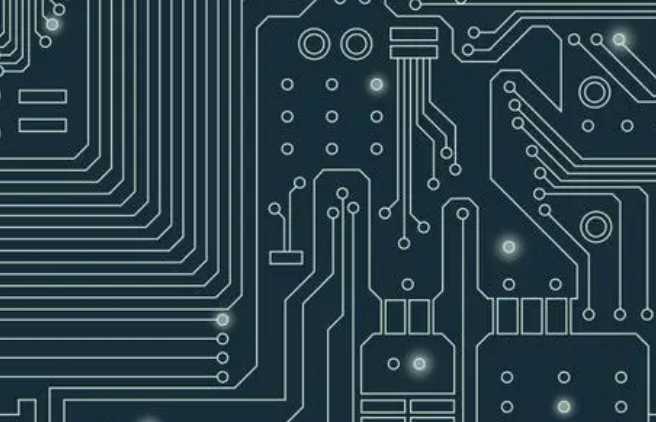
Uv laser cutting is an excellent choice for large or small scale production, as well as for PCB disassembly, especially for flexible or rigid-flexible circuit boards. Disassembly, in which individual circuit boards are removed from panels, is a challenge given the increasing flexibility of materials.
Mechanical disassembly methods such as V-slot cutting and automatic circuit board cutting are prone to damage sensitive and thin substrates, causing problems for electronic professional manufacturing services (EMS) companies when disassembling flexible and rigid circuit boards.
Ultraviolet laser cutting can not only eliminate the impact of mechanical stress produced in the process of cutting edge, deformation and damage circuit elements, but also less than the application of other laser disassembly, such as CO2 laser cutting thermal stress.
The reduction of "cut cushions" saves space, which means components can be placed closer to the edge of the circuit and more circuits can be installed on each board, maximizing efficiency and thus maximizing the limits of flexible circuit applications.
Application 3: Drilling
Another application that takes advantage of the small beam size and low stress properties of UV lasers is drilling, including through holes, microholes, and blind buried holes. Ultraviolet laser systems drill holes by focusing vertical beams and cutting straight through the substrate. Depending on the material used, holes as small as 10μm can be drilled.
Ultraviolet lasers are especially useful when drilling multiple layers. Multilayer PCBS are hot-die-cast together using composite materials. These so-called "semi-cures" can separate, especially after being processed with a higher temperature laser. However, the relatively stress-free nature of the UV laser solves this problem, as shown in Figure 4.
A 4mil diameter hole is drilled in a 14 mil multilayer board in the illustrated cross section. This application on a flexible polyimide copper-plated substrate showed no separation between the layers. There is another important point about the low stress properties of UV lasers: improved yield data. Yield The percentage of usable circuit boards removed from a panel.
There are many things that can cause damage to the board during the manufacturing process, including broken solder joints, broken components, or layering. Either of these factors could result in boards ending up in the waste bin on the production line rather than in the shipping bin.
Application 4: Deep Engraving
Another application that demonstrates the versatility of UV lasers is deep engraving, which involves a variety of forms. Using the software control of the laser system, the laser beam is set for controlled ablation, that is, the ability to cut a material at the desired depth and stop, continue, and complete the desired processing before moving to another depth and beginning another task.
Deep applications include small-scale manufacturing for embedding chips and surface grinding to remove organic materials from metal surfaces.
The ultraviolet laser can also perform multi step operation on the substrate. On polyethylene, the first step is to use a laser to create a groove with a depth of 2 mils, the second step is to create an 8 mils groove based on the previous step, and the third step is to create a 10mils groove. This illustrates the overall user control capabilities provided by the UV laser system.
Conclusion: A one-size-fits-all approach
The most remarkable thing about the ultraviolet laser is that it can do all of these applications in a single step. What does this mean for making circuit boards? Instead of using simultaneous processes and methods on different devices to complete an application, complete parts can be obtained in a single processing.
This streamlined production solution helps eliminate quality control issues that arise when boards are switched between different processes. The UV detrital ablation properties also mean that no post-processing cleaning is required.