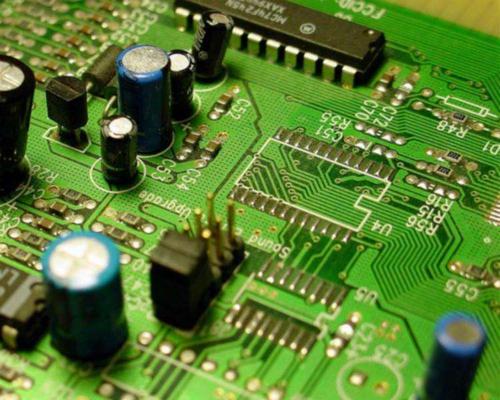
1, single-side circuit board process grinding → drilling → outer graphics → (full plate gilding) → etching → inspection → screen welding resistance → (hot air leveling) → screen printing characters → shape processing → test → inspection.
2, double-sided circuit board tin-spraying plate process grinding → drilling → copper thickening → outer graphics → tin plating, etching and tin removal → secondary drilling → inspection → screen welding resistance → gold-plated plug → hot air leveling → screen printing characters → shape processing → test → inspection.
3. Edge grinding → drilling → copper thickening → outer graphics → nickel plating and gold etching → secondary drilling → inspection → screen resistance welding → screen printing characters → shape processing → test → inspection.
4, multi-layer circuit board tin-spraying board process grinding → drilling positioning hole → inner graphic → inner etching → inspection → blackening → lamination → drilling → copper thickening → Outer graphic → tin plating, etching and tin removal → secondary drilling → inspection → screen printing resistance → gold-plated plug → hot air leveling → screen printing characters → shape processing → test → inspection.
5, multi-layer circuit board nickel plating plating process process edge grinding → drilling positioning holes → inner graphic → inner etching → inspection → blackening → lamination → drilling → copper plating thickening → Outer graphic → tin plating, etching and tin removal → secondary drilling → inspection → screen printing resistance → chemical nickel plating → screen printing characters → shape processing → test → inspection.
PCB board classification and parameter details
PCB board introduction: According to the brand quality level from bottom to high divided as follows: 94HB-94vo-CIM-1-CIM-3-FR-4
Detailed parameters and uses are as follows:
94HB: ordinary cardboard, not fireproof (the lowest grade material, die punching, can not do power board)
94V0: Flame retardant board (die punching)
22F: One side half glass fiber board (die punch)
Cim-1: single-side glass fiber board (must be drilled by computer, cannot die punch)
Cim-3: double-sided half-glass fiber board (except double-sided cardboard belongs to the lowest end of the double panel material, simple double panel can use this material, than FR-4 will be cheaper 5~10 yuan/square meter)
FR-4: Double-sided fiberglass board
1. The classification of flame retardant properties can be divided into four kinds: 94VO-V-1-V-2-94HB
2. Semi-cured sheet: 1080=0.0712mm, 2116=0.1143mm, 7628=0.1778mm
3. FR4 CIM-3 both represent plates, fr4 is fiberglass board, and cem3 is composite substrate
4. Halogen-free refers to the substrate that does not contain halogen (fluorobromine iodine and other elements), because bromine will produce toxic gas in combustion, environmental protection requirements.
5. Tg is the glass transformation temperature, that is, the melting point.
6. The circuit board must be inflammable, not burning at a certain temperature, can only be softened. The temperature point at this time is called the glass transition temperature (Tg point), and this value is related to the size and durability of PCB board.
What is high Tg? PCB circuit board and the advantages of using high Tg PCB:
When the temperature of high Tg printed circuit board rises to a certain threshold, the substrate will change from "glass state" to "rubber state", and the temperature at this time is called the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the board. That is, Tg is the highest temperature (° C) at which the substrate remains rigid. In other words, ordinary PCB substrate materials continue to produce softening, deformation, melting and other phenomena at high temperature, and also show a sharp decline in mechanical and electrical characteristics, which affects the service life of the product. Generally, the board of Tg is more than 130℃, the board of high Tg is generally more than 170℃, and the medium Tg is more than 150℃. Usually Tg≥170℃ PCB printed board, known as high Tg printed board; With the increase of Tg of the substrate, the characteristics of heat resistance, moisture resistance, chemical resistance and stability of the printed board will be enhanced and improved. The higher the TG value, the better the temperature resistance of the plate, especially in the lead-free process, high Tg is often used. High Tg means high heat resistance.
With the rapid development of the electronic industry, especially the electronic products represented by computers, towards high functional, high multilayer development, the need for PCB substrate material higher heat resistance as the premise. With the emergence and development of high density installation technology represented by SMT and CMT, PCB is increasingly dependent on the support of high heat resistance of substrate in terms of small aperture, fine line and thin shape.
Therefore, the difference between general FR-4 and high Tg: at the same high temperature, especially after hygroscopic heat, the material mechanical strength, dimensional stability, adhesion, water absorption, thermal decomposition, thermal expansion and other conditions are different, high Tg products are obviously better than ordinary PCB substrate materials.









