Both rigid and flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) are used to connect electronic components in various consumer and non-consumer devices. As the name suggests, a rigid PCBis a circuit board built on a rigid base layer that cannot be bent, while a flexible PCB (also known as a flex circuit) is built on a flexible base that can be bent, twisted, and folded.

Although both traditional and flexible PCBs serve the same basic purpose, it is important to note that there are many differences between them. Flex circuits are not just curved PCBs, they are manufactured differently than rigid PCBs and have various performance advantages and disadvantages. Learn more about Rigid PCBs vs. flexible PCBs below.
What is the difference between rigid PCB and flexible circuit?
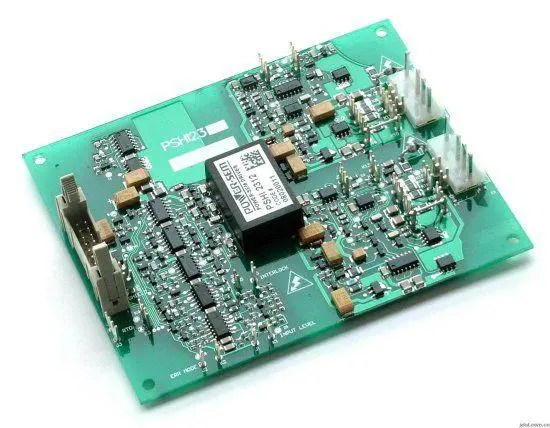
A rigid PCB, often referred to simply as a PCB, is what most people think of when they imagine a circuit board. These boards connect electrical components using conductive tracks and other elements arranged on a non-conductive substrate. On rigid circuit boards, the non-conductive substrate typically contains glass, which enhances the board and gives it strength and stiffness. Rigid circuit boards provide good support for components and provide good thermal resistance.
Although flexible PCBs also have conductive traces on non-conductive substrates, this type of circuit board uses a flexible substrate such as polyimide. The flexible base enables the flexible circuit to withstand vibration, dissipate heat and fold into various shapes. Due to their structural advantages, flexible circuits are increasingly used in compact and innovative electronic products.
In addition to the material and rigidity of the base layer, significant differences between PCBs and flex circuits include:
l Conductive material: Since flex circuits must be bent, manufacturers may use more flexible rolled annealed copper in place of conductive copper.
l Manufacturing process: Instead of solder mask, flex PCB manufacturers use a process called overlay or overlay to protect the exposed circuitry of the flex PCB.
l Typical cost: The cost of flexible circuits is usually higher than that of rigid circuit boards. However, because flexible circuit boards can be installed in tight spaces, engineers can downsize their products, resulting in indirect cost savings.
How to choose between rigid and flexible PCBs
Rigid and flexible circuit boards can be used in many different products, although some applications may benefit more from one type of circuit board. For example, rigid PCBs make sense in larger products such as televisions and desktop computers, while more compact products such as smartphones and wearable technology require flexible circuits.
When choosing between rigid and flexible PCBs, consider your application needs, the type of board the industry prefers, and the effect of using one type or the other may be profitable.